LangChain 讓 LLM 帶上記憶
最近兩年,我們見識了“百模大戰”,領略到了大型語言模型(LLM)的風采,但它們也存在一個顯著的缺陷:沒有記憶。
在對話中,無法記住上下文的 LLM 常常會讓用戶感到困擾。本文探討如何利用 LangChain,快速為 LLM 添加記憶能力,提升對話體驗。
LangChain 是 LLM 應用開發領域的最大社區和最重要的框架。

一、LLM 固有缺陷,沒有記憶
當前的 LLM 非常智能,在理解和生成自然語言方面表現優異,但是有一個顯著的缺陷:沒有記憶。
LLM 的本質是基于統計和概率來生成文本,對于每次請求,它們都將上下文視為獨立事件。這意味著當你與 LLM 進行對話時,它不會記住你之前說過的話,這就導致了 LLM 有時表現得不夠智能。
這種“無記憶”屬性使得 LLM 無法在長期對話中有效跟蹤上下文,也無法積累歷史信息。比如,當你在聊天過程中提到一個人名,后續再次提及該人時,LLM 可能會忘記你之前的描述。
本著發現問題解決問題的原則,既然沒有記憶,那就給 LLM 裝上記憶吧。
二、記憶組件的原理
1.沒有記憶的煩惱
當我們與 LLM 聊天時,它們無法記住上下文信息,比如下圖的示例:
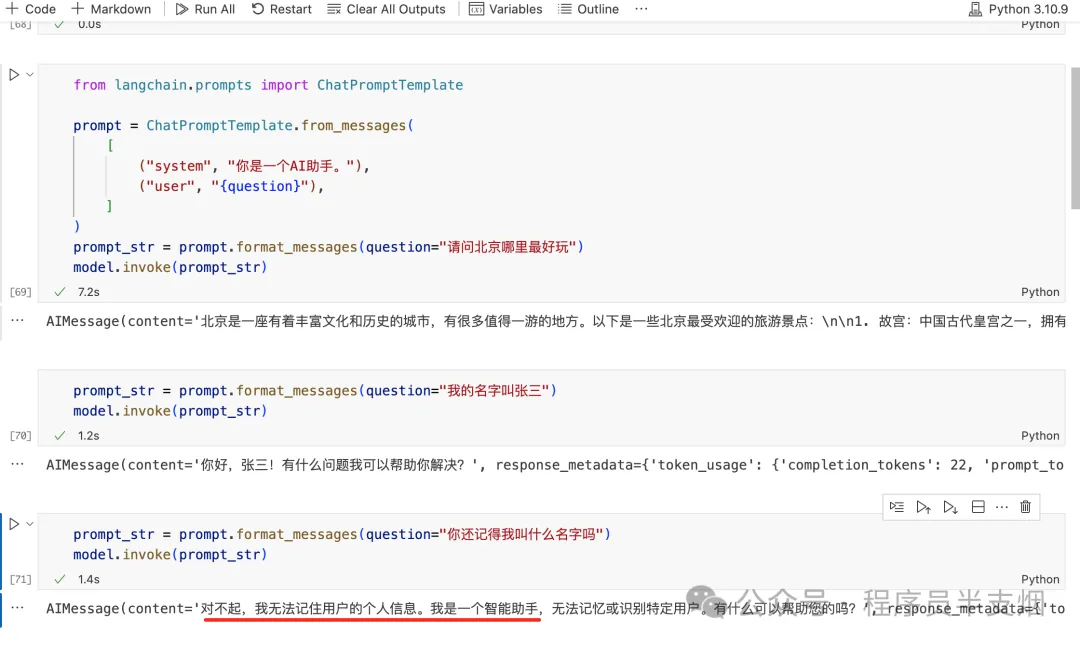
2.原理
如果將已有信息放入到 memory 中,每次跟 LLM 對話時,把已有的信息丟給 LLM,那么 LLM 就能夠正確回答,見如下示例:
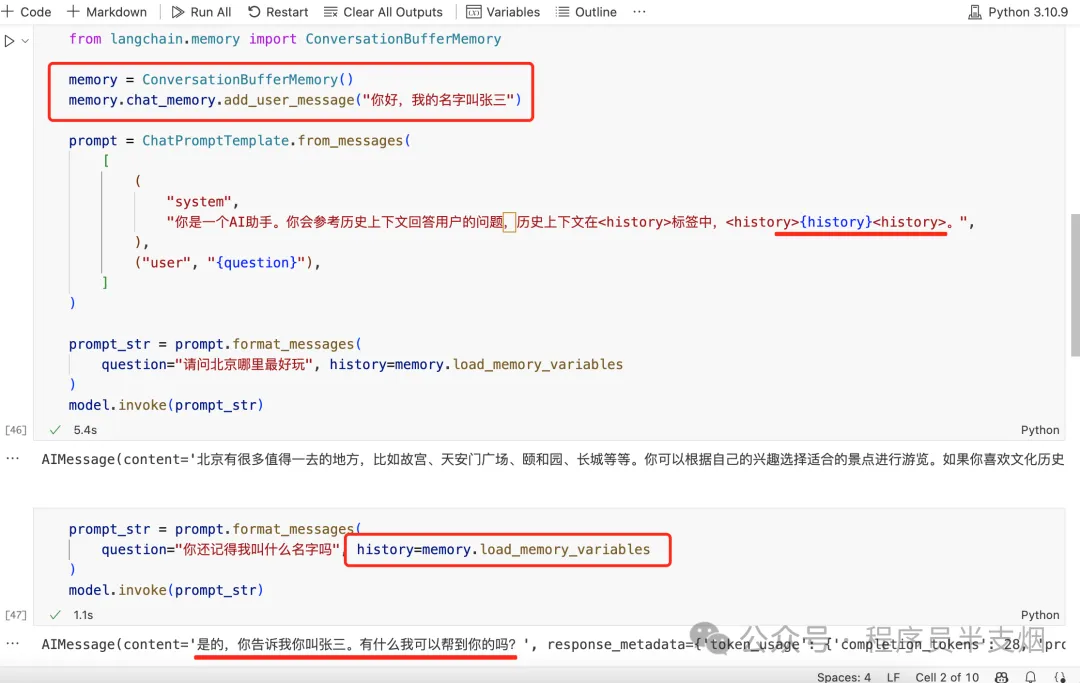
目前業內解決 LLM 記憶問題就是采用了類似上圖的方案,即:將每次的對話記錄再次丟入到 Prompt 里,這樣 LLM 每次對話時,就擁有了之前的歷史對話信息。
但如果每次對話,都需要自己手動將本次對話信息繼續加入到history信息中,那未免太繁瑣。有沒有輕松一些的方式呢?有,LangChain!LangChain 對記憶組件做了高度封裝,開箱即用。
3.長期記憶和短期記憶
在解決 LLM 的記憶問題時,有兩種記憶方案,長期記憶和短期記憶。
- 短期記憶:基于內存的存儲,容量有限,用于存儲臨時對話內容。
- 長期記憶:基于硬盤或者外部數據庫等方式,容量較大,用于存儲需要持久的信息。
三、LangChain 讓 LLM 記住上下文
LangChain 提供了靈活的內存組件工具來幫助開發者為 LLM 添加記憶能力。
1.單獨用 ConversationBufferMemory 做短期記憶
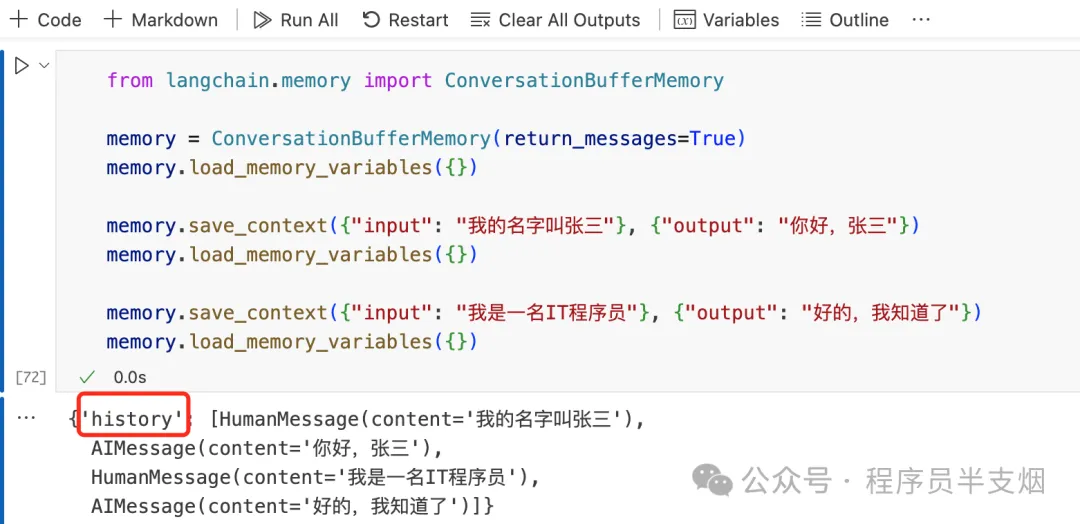
Langchain 提供了 ConversationBufferMemory 類,可以用來存儲和管理對話。
ConversationBufferMemory 包含input變量和output變量,input代表人類輸入,output代表 AI 輸出。
每次往ConversationBufferMemory組件里存入對話信息時,都會存儲到history的變量里。
2.利用 MessagesPlaceholder 手動添加 history
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True)
memory.load_memory_variables({})
memory.save_context({"input": "我的名字叫張三"}, {"output": "你好,張三"})
memory.load_memory_variables({})
memory.save_context({"input": "我是一名 IT 程序員"}, {"output": "好的,我知道了"})
memory.load_memory_variables({})
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "你是一個樂于助人的助手。"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
("human", "{user_input}"),
]
)
chain = prompt | model
user_input = "你知道我的名字嗎?"
history = memory.load_memory_variables({})["history"]
chain.invoke({"user_input": user_input, "history": history})
user_input = "中國最高的山是什么山?"
res = chain.invoke({"user_input": user_input, "history": history})
memory.save_context({"input": user_input}, {"output": res.content})
res = chain.invoke({"user_input": "我們聊得最后一個問題是什么?", "history": history})執行結果如下:

3.利用 ConversationChain 自動添加 history
我們利用 LangChain 的ConversationChain對話鏈,自動添加history的方式添加臨時記憶,無需手動添加。一個鏈實際上就是將一部分繁瑣的小功能做了高度封裝,這樣多個鏈就可以組合形成易用的強大功能。這里鏈的優勢一下子就體現出來了:
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True)
chain = ConversationChain(llm=model, memory=memory)
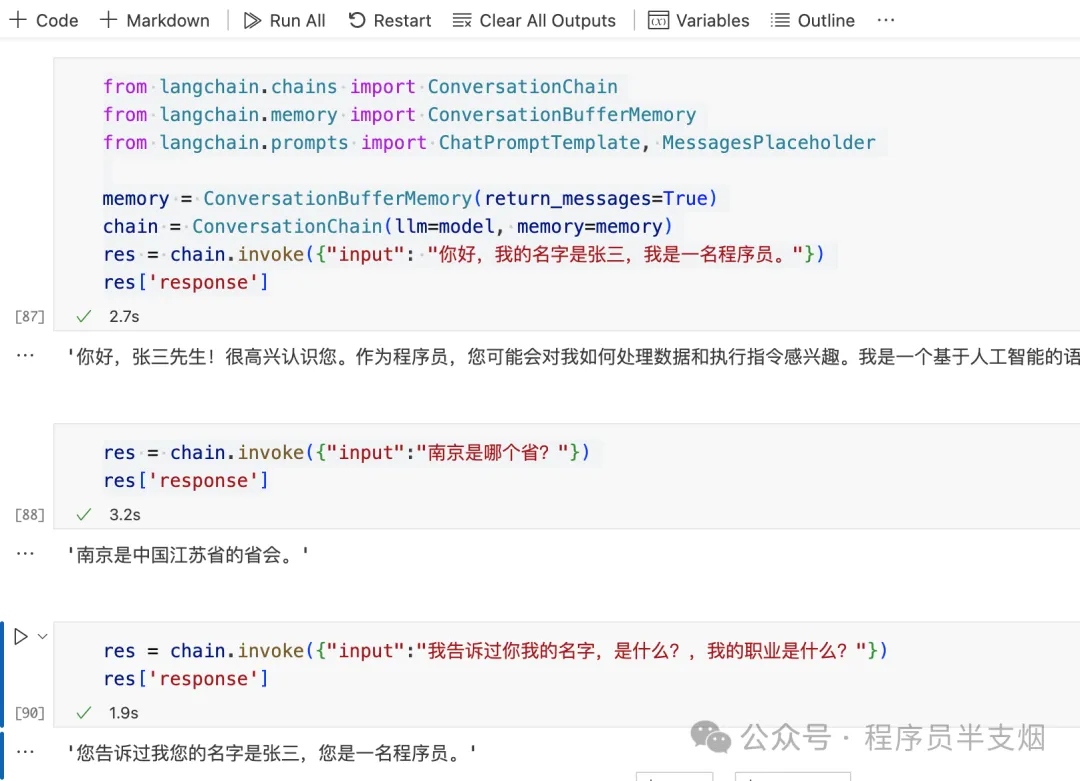
res = chain.invoke({"input": "你好,我的名字是張三,我是一名程序員。"})
res['response']
res = chain.invoke({"input":"南京是哪個省?"})
res['response']
res = chain.invoke({"input":"我告訴過你我的名字,是什么?,我的職業是什么?"})
res['response']執行結果如下,可以看到利用ConversationChain對話鏈,可以讓 LLM 快速擁有記憶:
4. 對話鏈結合 PromptTemplate 和 MessagesPlaceholder
在 Langchain 中,MessagesPlaceholder是一個占位符,用于在對話模板中動態插入上下文信息。它可以幫助我們靈活地管理對話內容,確保 LLM 能夠使用最上下文來生成響應。
采用ConversationChain對話鏈結合PromptTemplate和MessagesPlaceholder,幾行代碼就可以輕松讓 LLM 擁有短時記憶。
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "你是一個愛撒嬌的女助手,喜歡用可愛的語氣回答問題。"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
("human", "{input}"),
]
)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True)
chain = ConversationChain(llm=model, memory=memory, prompt=prompt)
res = chain.invoke({"input": "今天你好,我的名字是張三,我是你的老板"})
res['response']
res = chain.invoke({"input": "幫我安排一場今天晚上的高規格的晚飯"})
res['response']
res = chain.invoke({"input": "你還記得我叫什么名字嗎?"})
res['response']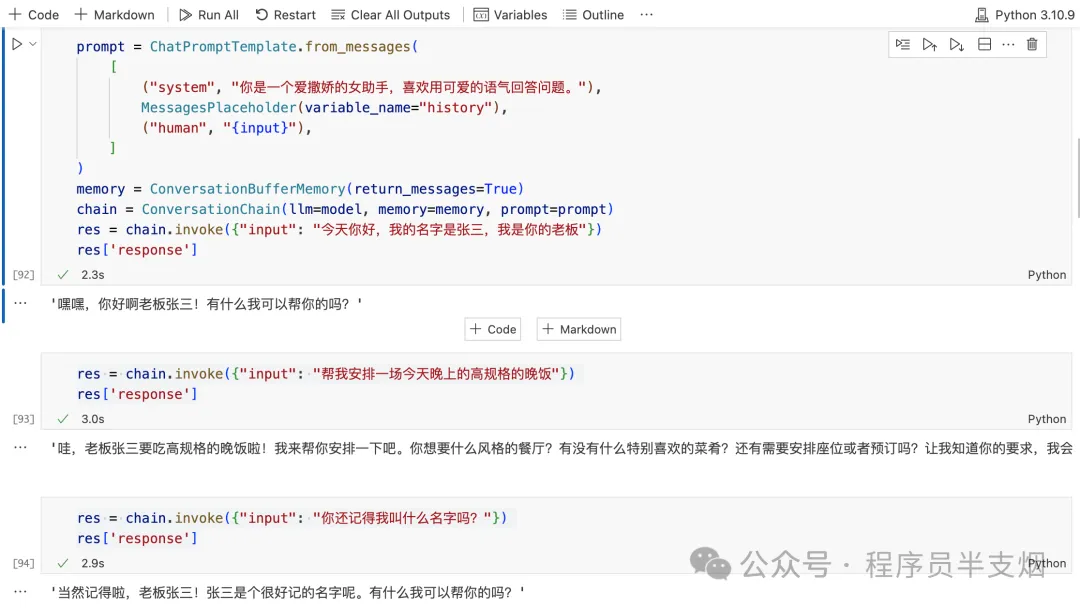
四、使用長期記憶
短期記憶在會話關閉或者服務器重啟后,就會丟失。如果想長期記住對話信息,只能采用長期記憶組件。
LangChain 支持多種長期記憶組件,比如Elasticsearch、MongoDB、Redis等,下面以Redis為例,演示如何使用長期記憶。
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import RedisChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
model = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
openai_api_key="sk-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
openai_api_base="https://api.aigc369.com/v1",
)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "你是一個擅長{ability}的助手"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
("human", "{question}"),
]
)
chain = prompt | model
chain_with_history = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
chain,
# 使用redis存儲聊天記錄
lambda session_id: RedisChatMessageHistory(
session_id, url="redis://10.20.1.10:6379/3"
),
input_messages_key="question",
history_messages_key="history",
)
# 每次調用都會保存聊天記錄,需要有對應的session_id
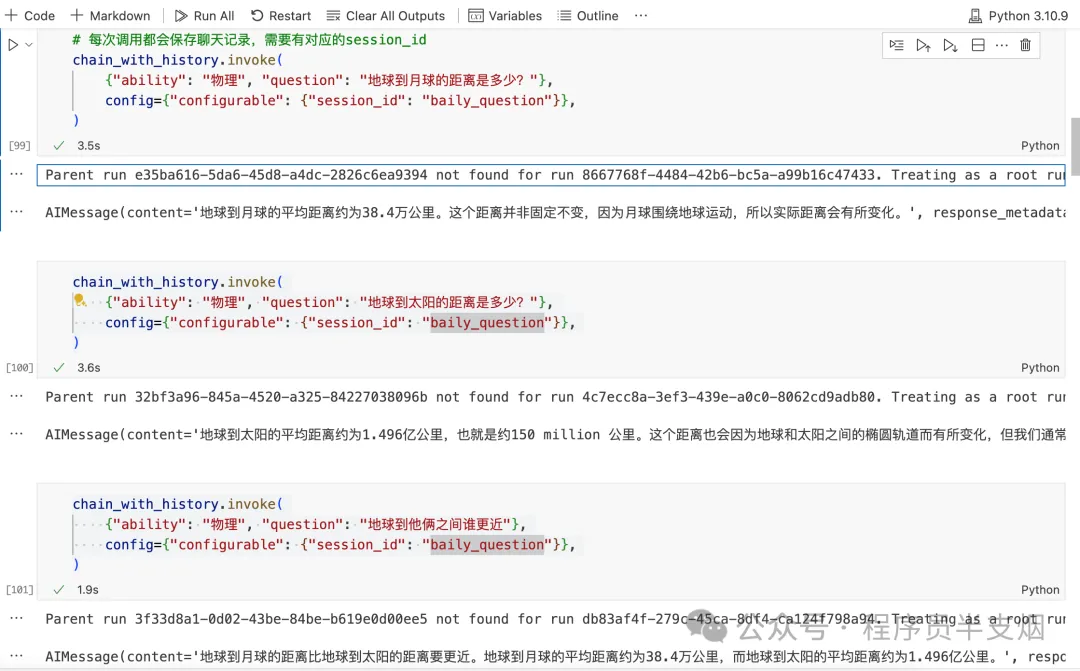
chain_with_history.invoke(
{"ability": "物理", "question": "地球到月球的距離是多少?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "baily_question"}},
)
chain_with_history.invoke(
{"ability": "物理", "question": "地球到太陽的距離是多少?"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "baily_question"}},
)
chain_with_history.invoke(
{"ability": "物理", "question": "地球到他倆之間誰更近"},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "baily_question"}},
)LLM 的回答如下,同時關閉 session 后,直接再次提問最后一個問題,LLM 仍然能給出正確答案。
只要configurable配置的session_id能對應上,LLM 就能給出正確答案。
然后,繼續查看redis存儲的數據,可以看到數據在 redis 中是以 list的數據結構存儲的。

五、總結
本文介紹了 LLM 缺乏記憶功能的固有缺陷,以及記憶組件的原理,還討論了如何利用 LangChain 給 LLM 裝上記憶組件,讓 LLM 能夠在對話中更好地保持上下文。希望對你有幫助!












































