為什么ThreadLocal容易導致內存泄漏?
本文轉載自微信公眾號「三不猴子」,作者sanbuhouzi。轉載本文請聯系三不猴子公眾號。
為什么ThreadLocal容易導致內存泄漏?
ThreadLocal是什么?
官方解釋為:
This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its get or set method) has its own, independently initialized copy of the variable.
我們通常創建的變量可以被任何線程訪問和修改,而是用ThreadLocal創建的變量只能通過當前線程去訪問和修改。
ThreadLocal原理
jdk版本1.8,我們先看一下ThreadLocal的源碼,先從set方法開始。
- /**
- * Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
- * to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
- * override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
- * method to set the values of thread-locals.
- *
- * @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
- * this thread-local.
- */
- public void set(T value) {
- Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
- ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
- if (map != null)
- map.set(this, value);
- else
- createMap(t, value);
- }
這個ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的一個內部類,key是當前Thread對象,value是我們要存的對象。首先拿到當前線程對象,然后獲取了個map,然后往這個map中放了當前ThreadLocal對象,如果map為空則創建一個map。看看getMap的邏輯。
- /**
- * Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
- * InheritableThreadLocal.
- *
- * @param t the current thread
- * @return the map
- */
- ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
- return t.threadLocals;
- }
getMap就是在Thread成員變量中獲取一個map。往下就是ThreadLocalMap.set()看看set的邏輯。
- /**
- * Set the value associated with key.
- *
- * @param key the thread local object
- * @param value the value to be set
- */
- private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
- // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
- // least as common to use set() to create new entries as
- // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
- // path would fail more often than not.
- Entry[] tab = table;
- int len = tab.length;
- int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
- for (Entry e = tab[i];
- e != null;
- e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
- ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
- if (k == key) {
- e.value = value;
- return;
- }
- if (k == null) {
- replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
- return;
- }
- }
- tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
- int sz = ++size;
- if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
- rehash();
- }
這里構造了個Entry對象,這個Entry可以看成是map的一行數據,一個key-value對。再看看Entry的源碼。
- static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
- /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
- Object value;
- Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
- super(k);
- value = v;
- }
- }
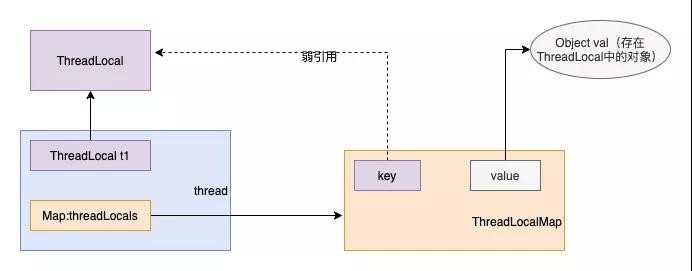
這個Entry對象竟然是繼承了WeakReference對象。上面的流程用圖畫出來就是這樣的。
總結起來就是:
- 每個Thread維護著一個ThreadLocalMap的引用
- ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的內部類,用Entry來進行存儲
- 調用ThreadLocal的set()方法時,實際上就是往ThreadLocalMap設置值,key是ThreadLocal對象,value是傳遞進來的對象
- 調用ThreadLocal的get()方法時,實際上就是往ThreadLocalMap獲取值,key是ThreadLocal對象
ThreadLocal本身并不存儲值,它只是作為一個key來讓線程從ThreadLocalMap獲取value。
什么是弱引用呢? 為什么ThreadLocal要使用弱引用呢?
官方文檔解釋為:
- /**
- * Weak reference objects, which do not prevent their referents from being
- * made finalizable, finalized, and then reclaimed. Weak references are most
- * often used to implement canonicalizing mappings.
- *
- * <p> Suppose that the garbage collector determines at a certain point in time
- * that an object is <a href="package-summary.html#reachability">weakly
- * reachable</a>. At that time it will atomically clear all weak references to
- * that object and all weak references to any other weakly-reachable objects
- * from which that object is reachable through a chain of strong and soft
- * references. At the same time it will declare all of the formerly
- * weakly-reachable objects to be finalizable. At the same time or at some
- * later time it will enqueue those newly-cleared weak references that are
- * registered with reference queues.
- *
- * @author Mark Reinhold
- * @since 1.2
- */
就是不會被程序計數器計數的引用,所以在垃圾回收器回收的時候不管是否有引用都會被回收。由于垃圾回收器是一個優先級很低的線程,因此不一定會很快發現那些只具有弱引用的對象。
ThreadLocal為什么要使用弱引用?
因為當我們存入的對象被置為null的時候,也就是ThreadLocalMap的value為null,ThreadLocalMap的key是弱引用此時在下一次垃圾回收器回收垃圾的時候就可以回收掉這個key-value也是就一個Entry對象了。
既然弱引用是有助于垃圾回收的,那為什么ThreadLocal還是容易導致內存泄漏?
弱引用確實是有助于垃圾回收,但是也是有弊端的,假設我們現在存入了一個對象,此時虛擬機gc,將key弱引用回收,但是value依然是強引用,key被回收了,這個value無法通過通過ThreadLocal對象的get方法獲取,它永遠不會被訪問到了,所以存在內存泄漏的風險。
如何避免內存泄漏
- 在ThreadLocal使用前后都調用remove清理,同時對異常情況也要在finally中清理。
- 盡量不要使用全局的ThreadLocal,靜態變量的生命周期和類的生命周期是一致的,而類的卸載時機可以說比較苛刻,這會導致靜態ThreadLocal無法被垃圾回收,容易出現內存泄漏。