SpringBoot 如何實現零拷貝:深度解析零拷貝技術
前言
一、為什么引入零拷貝?
如果服務端要提供文件傳輸的功能,我們能想到的最簡單的方式是:將磁盤上的文件讀取出來,然后通過網絡協議發送給客戶端。
傳統 I/O 的工作方式是,數據讀取和寫入是從用戶空間到內核空間來回復制,而內核空間的數據是通過操作系統層面的 I/O 接口從磁盤讀取或寫入。
C:
read(file, tmp_buf, len);
write(socket, tmp_buf, len);Java:
// 傳統文件讀取和發送的偽代碼表示
public class TraditionalFileTransfer {
public void transferFile(File file, Socket socket) throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = new byte[8192]; // 用戶空間緩沖區
// 1. 從磁盤讀取到內核緩沖區(DMA拷貝)
// 2. 從內核緩沖區拷貝到用戶緩沖區(CPU拷貝)
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
// 3. 從用戶緩沖區拷貝到Socket緩沖區(CPU拷貝)
// 4. 從Socket緩沖區拷貝到網卡緩沖區(DMA拷貝)
socket.getOutputStream().write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
}代碼很簡單,雖然就兩行代碼,但是這里面發生了不少的事情。
 圖片
圖片
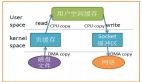
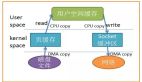
首先,期間共發生了 4 次用戶態與內核態的上下文切換,因為發生了兩次系統調用,一次是 read() ,一次是 write(),每次系統調用都得先從用戶態切換到內核態,等內核完成任務后,再從內核態切換回用戶態。
上下文切換到成本并不小,一次切換需要耗時幾十納秒到幾微秒,雖然時間看上去很短,但是在高并發的場景下,這類時間容易被累積和放大,從而影響系統的性能。
其次,還發生了 4 次數據拷貝,其中兩次是 DMA 的拷貝,另外兩次則是通過 CPU 拷貝的,下面說一下這個過程:
- 第一次拷貝,把磁盤上的數據拷貝到操作系統內核的緩沖區里,這個拷貝的過程是通過 DMA 搬運的。
- 第二次拷貝,把內核緩沖區的數據拷貝到用戶的緩沖區里,于是我們應用程序就可以使用這部分數據了,這個拷貝到過程是由 CPU 完成的。
- 第三次拷貝,把剛才拷貝到用戶的緩沖區里的數據,再拷貝到內核的 socket 的緩沖區里,這個過程依然還是由 CPU 搬運的。
- 第四次拷貝,把內核的 socket 緩沖區里的數據,拷貝到網卡的緩沖區里,這個過程又是由 DMA 搬運的。
我們回過頭看這個文件傳輸的過程,我們只是搬運一份數據,結果卻搬運了 4 次,過多的數據拷貝無疑會消耗 CPU 資源,大大降低了系統性能。
這種簡單又傳統的文件傳輸方式,存在冗余的上文切換和數據拷貝,在高并發系統里是非常糟糕的,多了很多不必要的開銷,會嚴重影響系統性能。
所以,要想提高文件傳輸的性能,就需要減少「用戶態與內核態的上下文切換」和「內存拷貝」的次數。
零拷貝原理
一、mmap + write 實現零拷貝
在前面我們知道,read() 系統調用的過程中會把內核緩沖區的數據拷貝到用戶的緩沖區里,于是為了減少這一步開銷,我們可以用 mmap() 替換 read() 系統調用函數。
buf = mmap(file, len);
write(sockfd, buf, len);mmap() 系統調用函數會直接把內核緩沖區里的數據「映射」到用戶空間,這樣,操作系統內核與用戶空間就不需要再進行任何的數據拷貝操作。
 圖片
圖片
具體過程如下:
- 應用進程調用了 mmap() 后,DMA 會把磁盤的數據拷貝到內核的緩沖區里。接著,應用進程跟操作系統內核「共享」這個緩沖區;
- 應用進程再調用 write(),操作系統直接將內核緩沖區的數據拷貝到 socket 緩沖區中,這一切都發生在內核態,由 CPU 來搬運數據;
- 最后,把內核的 socket 緩沖區里的數據,拷貝到網卡的緩沖區里,這個過程是由 DMA 搬運的。
我們可以得知,通過使用 mmap() 來代替 read(), 可以減少一次數據拷貝的過程。
但這還不是最理想的零拷貝,因為仍然需要通過 CPU 把內核緩沖區的數據拷貝到 socket 緩沖區里,而且仍然需要 4 次上下文切換,因為系統調用還是 2 次。
二、sendfile 實現零拷貝
在 Linux 內核版本 2.1 中,提供了一個專門發送文件的系統調用函數 sendfile(),函數形式如下:
#include <sys/socket.h>
ssize_t sendfile(int out_fd, int in_fd, off_t *offset, size_t count);它的前兩個參數分別是目的端和源端的文件描述符,后面兩個參數是源端的偏移量和復制數據的長度,返回值是實際復制數據的長度。
首先,它可以替代前面的 read() 和 write() 這兩個系統調用,這樣就可以減少一次系統調用,也就減少了 2 次上下文切換的開銷。
其次,該系統調用,可以直接把內核緩沖區里的數據拷貝到 socket 緩沖區里,不再拷貝到用戶態,這樣就只有 2 次上下文切換,和 3 次數據拷貝。如下圖:
 圖片
圖片
但是這還不是真正的零拷貝技術,如果網卡支持 SG-DMA(The Scatter-Gather Direct Memory Access)技術(和普通的 DMA 有所不同),我們可以進一步減少通過 CPU 把內核緩沖區里的數據拷貝到 socket 緩沖區的過程。
你可以在你的 Linux 系統通過下面這個命令,查看網卡是否支持 scatter-gather 特性:
$ ethtool -k eth0 | grep scatter-gather
scatter-gather: on于是,從 Linux 內核 2.4 版本開始起,對于支持網卡支持 SG-DMA 技術的情況下, sendfile() 系統調用的過程發生了點變化,具體過程如下:
- 第一步,通過 DMA 將磁盤上的數據拷貝到內核緩沖區里;
- 第二步,緩沖區描述符和數據長度傳到 socket 緩沖區,這樣網卡的 SG-DMA 控制器就可以直接將內核緩存中的數據拷貝到網卡的緩沖區里,此過程不需要將數據從操作系統內核緩沖區拷貝到 socket 緩沖區中,這樣就減少了一次數據拷貝;
所以,這個過程之中,只進行了 2 次數據拷貝,如下圖:
 圖片
圖片
這就是所謂的零拷貝(Zero-copy)技術,因為我們沒有在內存層面去拷貝數據,也就是說全程沒有通過 CPU 來搬運數據,所有的數據都是通過 DMA 來進行傳輸的。
零拷貝技術的文件傳輸方式相比傳統文件傳輸的方式,減少了 2 次上下文切換和數據拷貝次數,只需要 2 次上下文切換和數據拷貝次數,就可以完成文件的傳輸,而且 2 次的數據拷貝過程,都不需要通過 CPU,2 次都是由 DMA 來搬運。
SpringBoot 零拷貝實現
一、基于NIO的FileChannel實現
核心文件傳輸服務
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ZeroCopyFileService {
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
/**
* 使用FileChannel.transferTo實現零拷貝文件傳輸
* 這是最高效的零拷貝實現方式
*/
public void transferFileWithZeroCopy(File file, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException {
try (FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(file).getChannel();
WritableByteChannel outputChannel = Channels.newChannel(response.getOutputStream())) {
long position = 0;
long fileSize = fileChannel.size();
// 使用transferTo進行零拷貝傳輸
while (position < fileSize) {
long transferred = fileChannel.transferTo(position, fileSize - position, outputChannel);
if (transferred <= 0) {
break;
}
position += transferred;
}
log.debug("零拷貝文件傳輸完成: {}, 文件大小: {} bytes", file.getName(), fileSize);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("零拷貝文件傳輸失敗: {}", file.getName(), e);
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 使用MappedByteBuffer實現內存映射文件傳輸
* 適合大文件的分塊處理
*/
public void transferFileWithMmap(File file, ServletResponse response,
long chunkSize) throws IOException {
if (chunkSize <= 0) {
chunkSize = 1024 * 1024; // 默認1MB分塊
}
try (FileChannel fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r").getChannel()) {
long fileSize = fileChannel.size();
long position = 0;
while (position < fileSize) {
long size = Math.min(chunkSize, fileSize - position);
// 創建內存映射
MappedByteBuffer mappedBuffer = fileChannel.map(
FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, position, size);
// 通過Channel發送映射的緩沖區
WritableByteChannel outputChannel = Channels.newChannel(response.getOutputStream());
while (mappedBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
outputChannel.write(mappedBuffer);
}
// 清理映射
clean(mappedBuffer);
position += size;
}
log.debug("內存映射文件傳輸完成: {}, 文件大小: {} bytes", file.getName(), fileSize);
}
}
/**
* 清理MappedByteBuffer
*/
private void clean(MappedByteBuffer buffer) {
if (buffer == null || !buffer.isDirect()) return;
try {
Method cleanerMethod = buffer.getClass().getMethod("cleaner");
cleanerMethod.setAccessible(true);
Object cleaner = cleanerMethod.invoke(buffer);
if (cleaner != null) {
Method cleanMethod = cleaner.getClass().getMethod("clean");
cleanMethod.setAccessible(true);
cleanMethod.invoke(cleaner);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("清理MappedByteBuffer失敗", e);
}
}
}二、Spring Web 零拷貝控制器實現
RESTful文件傳輸接口
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/file")
@Slf4j
public class ZeroCopyFileController {
@Autowired
private ZeroCopyFileService zeroCopyFileService;
@Value("${file.upload.dir:/tmp/uploads}")
private String uploadDir;
/**
* 零拷貝文件下載
*/
@GetMapping("/download/{filename}")
public void downloadFile(@PathVariable String filename,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
File file = new File(uploadDir, filename);
if (!file.exists() || !file.isFile()) {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), "文件不存在");
return;
}
// 設置響應頭
setupFileDownloadHeaders(response, file, filename);
try {
// 使用零拷貝傳輸文件
zeroCopyFileService.transferFileWithZeroCopy(file, response);
log.info("文件下載完成: {}, 大小: {} bytes, 客戶端: {}",
filename, file.length(), getClientIp(request));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("文件下載失敗: {}", filename, e);
if (!response.isCommitted()) {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(),
"文件下載失敗");
}
}
}
/**
* 大文件分塊下載(支持斷點續傳)
*/
@GetMapping("/download/{filename}/chunked")
public void downloadFileChunked(@PathVariable String filename,
@RequestHeader(value = "Range", required = false) String rangeHeader,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
File file = new File(uploadDir, filename);
if (!file.exists() || !file.isFile()) {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), "文件不存在");
return;
}
long fileLength = file.length();
long start = 0;
long end = fileLength - 1;
// 處理范圍請求(斷點續傳)
if (rangeHeader != null && rangeHeader.startsWith("bytes=")) {
String[] ranges = rangeHeader.substring(6).split("-");
start = Long.parseLong(ranges[0]);
if (ranges.length > 1) {
end = Long.parseLong(ranges[1]);
}
end = Math.min(end, fileLength - 1);
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.PARTIAL_CONTENT.value());
response.setHeader("Content-Range",
String.format("bytes %d-%d/%d", start, end, fileLength));
}
long contentLength = end - start + 1;
setupFileDownloadHeaders(response, file, filename);
response.setContentLengthLong(contentLength);
// 使用內存映射進行分塊傳輸
try (RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel()) {
// 定位到指定位置
WritableByteChannel outputChannel = Channels.newChannel(response.getOutputStream());
fileChannel.transferTo(start, contentLength, outputChannel);
log.info("文件分塊下載完成: {} [{} - {}], 客戶端: {}",
filename, start, end, getClientIp(request));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("文件分塊下載失敗: {}", filename, e);
if (!response.isCommitted()) {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(),
"文件下載失敗");
}
}
}
/**
* 設置文件下載響應頭
*/
private void setupFileDownloadHeaders(HttpServletResponse response,
File file, String filename) {
// 內容類型
String contentType = determineContentType(filename);
response.setContentType(contentType);
// 內容處置
String encodedFilename = URLEncoder.encode(filename, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
.replaceAll("\\+", "%20");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition",
"attachment; filename*=UTF-8''" + encodedFilename);
// 緩存控制
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "private, max-age=300");
response.setHeader("Pragma", "private");
response.setDateHeader("Expires",
System.currentTimeMillis() + 300 * 1000);
// 文件大小
response.setContentLengthLong(file.length());
// 支持斷點續傳
response.setHeader("Accept-Ranges", "bytes");
}
/**
* 根據文件名確定內容類型
*/
private String determineContentType(String filename) {
String extension = FilenameUtils.getExtension(filename).toLowerCase();
switch (extension) {
case "pdf": return "application/pdf";
case "jpg": case "jpeg": return "image/jpeg";
case "png": return "image/png";
case "txt": return "text/plain";
case "zip": return "application/zip";
default: return "application/octet-stream";
}
}
/**
* 獲取客戶端IP
*/
private String getClientIp(HttpServletRequest request) {
String xForwardedFor = request.getHeader("X-Forwarded-For");
if (xForwardedFor != null && !xForwardedFor.isEmpty()) {
return xForwardedFor.split(",")[0];
}
return request.getRemoteAddr();
}
}三、高級特性:異步零拷貝處理
異步文件處理器
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AsyncZeroCopyProcessor {
@Autowired
private ZeroCopyFileService zeroCopyFileService;
private final ExecutorService asyncExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("zero-copy-async-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
);
/**
* 異步零拷貝文件處理
*/
public CompletableFuture<Void> processFileAsync(File file,
ServletResponse response) {
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
zeroCopyFileService.transferFileWithZeroCopy(file, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("異步文件處理失敗: {}", file.getName(), e);
throw new CompletionException(e);
}
}, asyncExecutor);
}
/**
* 批量文件異步傳輸
*/
public CompletableFuture<Void> processBatchFilesAsync(List<File> files,
ServletResponse response) {
List<CompletableFuture<Void>> futures = files.stream()
.map(file -> processFileAsync(file, response))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return CompletableFuture.allOf(
futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])
);
}
@PreDestroy
public void shutdown() {
asyncExecutor.shutdown();
try {
if (!asyncExecutor.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
asyncExecutor.shutdownNow();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
asyncExecutor.shutdownNow();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}四、Netty 零拷貝集成
Netty文件服務器實現
@Component
@Slf4j
public class NettyZeroCopyServer {
@Value("${netty.server.port:8080}")
private int port;
private EventLoopGroup bossGroup;
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
private ChannelFuture channelFuture;
/**
* 啟動Netty零拷貝文件服務器
*/
@PostConstruct
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));
pipeline.addLast(new ZeroCopyFileHandler());
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
log.info("Netty零拷貝文件服務器啟動成功,端口: {}", port);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Netty服務器啟動失敗", e);
stop();
throw e;
}
}
/**
* Netty零拷貝文件處理器
*/
private static class ZeroCopyFileHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) {
if (!request.decoderResult().isSuccess()) {
sendError(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
return;
}
if (request.method() != HttpMethod.GET) {
sendError(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED);
return;
}
String uri = request.uri();
if (!uri.startsWith("/file/")) {
sendError(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
String filename = uri.substring(6); // 去掉"/file/"
File file = new File("/data/files", filename);
if (!file.exists() || file.isDirectory()) {
sendError(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
// 使用零拷貝發送文件
try {
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
long fileLength = raf.length();
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK);
HttpUtil.setContentLength(response, fileLength);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/octet-stream");
// 設置文件下載頭
String encodedFilename = URLEncoder.encode(filename, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
.replaceAll("\\+", "%20");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_DISPOSITION,
"attachment; filename*=UTF-8''" + encodedFilename);
// 寫入HTTP響應頭
ctx.write(response);
// 使用零拷貝發送文件內容
FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(raf.getChannel(), 0, fileLength);
ctx.write(region, ctx.newProgressivePromise())
.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
log.error("文件傳輸失敗: {}", filename, future.cause());
}
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.warn("關閉文件失敗: {}", filename, e);
}
}
});
// 寫入結束標記
ChannelFuture lastContentFuture = ctx.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT);
lastContentFuture.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
log.debug("Netty零拷貝文件發送完成: {}, 大小: {} bytes", filename, fileLength);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("文件處理失敗: {}", filename, e);
sendError(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
private void sendError(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpResponseStatus status) {
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(
HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, status);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8");
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
log.error("通道處理異常", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
/**
* 停止服務器
*/
@PreDestroy
public void stop() {
if (channelFuture != null) {
channelFuture.channel().close();
}
if (bossGroup != null) {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
if (workerGroup != null) {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
log.info("Netty零拷貝文件服務器已停止");
}
}最佳實踐與注意事項
一、配置優化
零拷貝相關配置
# application.yml
server:
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: 10MB
max-request-size: 10MB
tomcat:
max-swallow-size: 10MB
max-http-form-post-size: 10MB
# 自定義零拷貝配置
zerocopy:
enabled: true
buffer-size: 8192
chunk-size: 1MB
max-file-size: 1GB
async-enabled: true
async-threads: 4二、內存管理優化
直接內存監控與管理
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DirectMemoryMonitor {
private final BufferPoolMXBean directBufferPool;
public DirectMemoryMonitor() {
this.directBufferPool = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMXBeans(BufferPoolMXBean.class)
.stream()
.filter(pool -> "direct".equals(pool.getName()))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
}
/**
* 監控直接內存使用情況
*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000)
public void monitorDirectMemory() {
if (directBufferPool != null) {
long used = directBufferPool.getMemoryUsed();
long total = directBufferPool.getTotalCapacity();
long count = directBufferPool.getCount();
if (used > total * 0.8) {
log.warn("直接內存使用率過高: {}/{} bytes ({} buffers)", used, total, count);
}
log.debug("直接內存使用: {}/{} bytes, 緩沖區數量: {}", used, total, count);
}
}
/**
* 獲取直接內存統計
*/
public DirectMemoryStats getDirectMemoryStats() {
if (directBufferPool == null) {
return null;
}
DirectMemoryStats stats = new DirectMemoryStats();
stats.setUsedMemory(directBufferPool.getMemoryUsed());
stats.setTotalCapacity(directBufferPool.getTotalCapacity());
stats.setBufferCount(directBufferPool.getCount());
stats.setUsagePercentage((double) stats.getUsedMemory() / stats.getTotalCapacity() * 100);
return stats;
}
@Data
public static class DirectMemoryStats {
private long usedMemory;
private long totalCapacity;
private long bufferCount;
private double usagePercentage;
}
}