Kmp 內(nèi)存分配和 GC 優(yōu)化分析和實(shí)踐

引言
K/N 的內(nèi)存管理器和 GC,和主流虛擬機(jī)基本一樣,主要功能如下:
- K/N 使用自己的 custom 內(nèi)存分配器,每個(gè)線程有自己的 tlab
- 默認(rèn)垃圾回收器通過(guò) Stop-the-world 標(biāo)記和并發(fā)清除收集器,并且不會(huì)將堆分代
- 當(dāng)前只支持弱引用,當(dāng)標(biāo)記階段完成后,GC 會(huì)處理弱引用,并使指向未標(biāo)記對(duì)象的引用無(wú)效
要監(jiān)控 GC 性能,需要在 Gradle 構(gòu)建腳本中設(shè)置以下編譯器選項(xiàng)。
代碼塊:
-Xruntime-logs=gc=info為了提高 GC 性能,可以在 Gradle 構(gòu)建腳本啟用 cms 垃圾回收器,將存活對(duì)象標(biāo)記與應(yīng)用程序線程并行運(yùn)行,減少 GC 暫停時(shí)間。
代碼塊:
kotlin.native.binary.gc=cms從文檔看,內(nèi)存分配器已經(jīng)比較完善了,但是 GC 性能比較差,默認(rèn)垃圾回收器是 STW,cms 還需要手動(dòng)配置。我們從代碼層面看一下。
Runtime
通過(guò)抓取過(guò) kmp trace,可以看到 runtime 入口。
- 鴻蒙 linker 是 ld-musl-aarch64.so,加載 libbenchmark.so,這是 kmp 的編譯產(chǎn)物
- 之后執(zhí)行 workRoutine 方法,這是 Runtime 的入口方法

抖音倉(cāng)庫(kù)用的是 kotlin2.0.20, workerRoutine 代碼在 kotlin-native 項(xiàng)目 Worker.cpp 文件。
- 先調(diào)用 Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded 初始化 Runtime
- 然后通過(guò) do/while 循環(huán)調(diào)用 processQueueElement 處理任務(wù),類似消息循環(huán)
代碼塊:
void* workerRoutine(void* argument){
Worker* worker = reinterpret_cast<Worker*>(argument);
// Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded calls WorkerInit that needs
// to see there's already a worker created for this thread.
::g_worker = worker;
Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded();
// Only run this routine in the runnable state. The moment between this routine exiting and thread
// destructors running will be spent in the native state. `Kotlin_deinitRuntimeCallback` ensures
// that runtime deinitialization switches back to the runnable state.
kotlin::ThreadStateGuard guard(worker->memoryState(), ThreadState::kRunnable);
do {
if (worker->processQueueElement(true) == JOB_TERMINATE) break;
} while (true);
returnnullptr;
}而 Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded 會(huì)調(diào)用 initRuntime,每個(gè)線程有獨(dú)立的 runtimeState 變量,通過(guò)判斷 runtimeState 變量狀態(tài)避免多次調(diào)用 initRuntime。
代碼塊:
RUNTIME_NOTHROW voidKotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded(){
if (!isValidRuntime()) {
initRuntime();
// Register runtime deinit function at thread cleanup.
konan::onThreadExit(Kotlin_deinitRuntimeCallback, runtimeState);
}
}
THREAD_LOCAL_VARIABLE RuntimeState* runtimeState = kInvalidRuntime;
inlineboolisValidRuntime(){
return ::runtimeState != kInvalidRuntime;
}initRuntime 具體功能如下:
- SetKonanTerminateHandler 為線程設(shè)置異常處理 Handler,這樣可以捕獲 kotlin excepiton
- 設(shè)置 runtimeState
- initializeGlobalRuntimeIfNeeded 初始化全局變量
- InitMemory 初始化線程內(nèi)存分配器
- WorkInit 初始化
代碼塊:
RuntimeState* initRuntime(){
SetKonanTerminateHandler();
RuntimeState* result = new RuntimeState();
if (!result) return kInvalidRuntime;
::runtimeState = result;
bool firstRuntime = initializeGlobalRuntimeIfNeeded();
result->memoryState = InitMemory();
// Switch thread state because worker and globals inits require the runnable state.
// This call may block if GC requested suspending threads.
ThreadStateGuard stateGuard(result->memoryState, kotlin::ThreadState::kRunnable);
result->worker = WorkerInit(result->memoryState);
result->status = RuntimeStatus::kRunning;
return result;
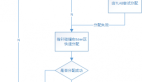
}initRuntime 過(guò)程如圖,我們接下來(lái)分別分析。

ExceptionHandler
SetKonanTerminateHandler 通過(guò) TerminateHandler 調(diào)用 std::set_terminate 設(shè)置 kotlinHandler 來(lái)處理異常。
代碼塊:
// Use one public function to limit access to the class declaration
voidSetKonanTerminateHandler(){
TerminateHandler::install();
}
/// Use machinery like Meyers singleton to provide thread safety
TerminateHandler()
: queuedHandler_((QH)std::set_terminate(kotlinHandler)) {}GlobalData
initializeGlobalRuntimeIfNeeded 調(diào)用 initGlobalMemory 初始化 GlobalData,GlobalData 包括 allocator_內(nèi)存分配器,gc_垃圾回收器,threadRegistry_線程列表等。GlobalData 是全局變量,所有線程共用,還有 ThreadData 是線程私有的,后續(xù)分析。
代碼塊:
voidkotlin::initGlobalMemory()noexcept{
mm::GlobalData::init();
}
// Global (de)initialization is undefined in C++. Use single global singleton to define it for simplicity.
classGlobalData :private Pinned {
public:
ThreadRegistry& threadRegistry()noexcept{ return threadRegistry_; }
GlobalsRegistry& globalsRegistry()noexcept{ return globalsRegistry_; }
SpecialRefRegistry& specialRefRegistry()noexcept{ return specialRefRegistry_; }
gcScheduler::GCScheduler& gcScheduler()noexcept{ return gcScheduler_; }
alloc::Allocator& allocator()noexcept{ return allocator_; }
gc::GC& gc()noexcept{ return gc_; }ThreadData
InitMemory 通過(guò)上面分析的 ThreadRegistry 全局變量的 RegisterCurrentThread 方法,生成 ThreadData,并注冊(cè)到 list_列表里,這樣 gc 時(shí)可以訪問(wèn)到 ThreadData 中的 gc root。currentThreadDataNode 是 thread local 變量,每個(gè)線程有獨(dú)立的變量。
代碼塊:
extern"C"MemoryState* InitMemory(){
mm::GlobalData::waitInitialized();
return mm::ToMemoryState(mm::ThreadRegistry::Instance().RegisterCurrentThread());
}
mm::ThreadRegistry::Node* mm::ThreadRegistry::RegisterCurrentThread() noexcept {
auto lock = list_.LockForIter();
auto* threadDataNode = list_.Emplace(konan::currentThreadId());
Node*& currentDataNode = currentThreadDataNode_;
currentDataNode = threadDataNode;
threadDataNode->Get()->gc().onThreadRegistration();
return threadDataNode;
}
// static
THREAD_LOCAL_VARIABLE mm::ThreadRegistry::Node* mm::ThreadRegistry::currentThreadDataNode_ = nullptr;ThreadData 包括 threadId_,allocator_, gc_等,每個(gè)線程一個(gè)對(duì)象,這樣 allocator_每個(gè)線程私有就實(shí)現(xiàn)了 tlab。
代碼塊:
// `ThreadData` is supposed to be thread local singleton.
// Pin it in memory to prevent accidental copying.
classThreadDatafinal : privatePinned{
public:
explicit ThreadData(int threadId) noexcept :
threadId_(threadId),
globalsThreadQueue_(GlobalsRegistry::Instance()),
specialRefRegistry_(SpecialRefRegistry::instance()),
gcScheduler_(GlobalData::Instance().gcScheduler(), *this),
allocator_(GlobalData::Instance().allocator()),
gc_(GlobalData::Instance().gc(), *this),
suspensionData_(ThreadState::kNative, *this){}總結(jié)一下,ThreadData 在每個(gè)線程內(nèi)部定義了內(nèi)存分配器和 GC,關(guān)于內(nèi)存分配器我們后續(xù)分析。

WorkInit
WorkInit 將 Work 的 thread_變量設(shè)置為線程自己,workRoutine 通過(guò) pthread_create 創(chuàng)建新線程 thread_來(lái)執(zhí)行。線程通過(guò) kotlin 代碼/c++代碼創(chuàng)建,創(chuàng)建好線程之后調(diào)用 initRuntime 來(lái)初始化。
代碼塊:
Worker* WorkerInit(MemoryState* memoryState){
Worker* worker;
if (::g_worker != nullptr) {
worker = ::g_worker;
} else {
worker = theState()->addWorkerUnlocked(workerExceptionHandling(), nullptr, WorkerKind::kOther);
::g_worker = worker;
}
worker->setThread(pthread_self());
worker->setMemoryState(memoryState);
return worker;
}
voidWorker::startEventLoop(){
kotlin::ThreadStateGuard guard(ThreadState::kNative);
pthread_create(&thread_, nullptr, workerRoutine, this);
}這里有個(gè)問(wèn)題,既然 workerRoutine 通過(guò) runtime 初始化調(diào)用,哪里真正調(diào)用 Runtime 呢?
CodeGenerator 會(huì)將每個(gè)方法中的 kotlin ir 轉(zhuǎn)換為 llvm ir,在這個(gè)過(guò)程中會(huì)插入 initRuntimeIfNeeded 調(diào)用。所以每個(gè)方法執(zhí)行時(shí)都會(huì)先調(diào)用 initRuntimeIfNeeded。
代碼塊:
if (needsRuntimeInit || switchToRunnable) {
check(!forbidRuntime) { "Attempt to init runtime where runtime usage is forbidden" }
call(llvm.initRuntimeIfNeeded, emptyList())
}Runtime 這里分析完了,我們繼續(xù)看一下 allocator_內(nèi)存分配器。
內(nèi)存分配
K/N 有 3 種內(nèi)存分配器:
- Custom:K/N 自己開發(fā)的內(nèi)存分配器,也是默認(rèn)的內(nèi)存分配器
- Std:標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫(kù)內(nèi)存分配器,在鴻蒙上是 jemalloc
- Mimalloc:mimalloc 是微軟開源的 native 分配器
每個(gè)內(nèi)存分配器都會(huì)實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè) Allocator::ThreadData::Impl 類,比如 CustomAllocator 就對(duì)應(yīng) Custom 內(nèi)存分配器,這樣 allocator_可以和特定的內(nèi)存分配器關(guān)聯(lián)。
代碼塊:
classAllocator::ThreadData::Impl : private Pinned {
public:
explicitImpl(Allocator::Impl& allocator)noexcept : alloc_(allocator.heap()){}
alloc::CustomAllocator& alloc()noexcept{ return alloc_; }
private:
CustomAllocator alloc_;
};
ALWAYS_INLINE ObjHeader* alloc::Allocator::ThreadData::allocateObject(const TypeInfo* typeInfo) noexcept {
return impl_->alloc().CreateObject(typeInfo);
}我們主要看一下 Custom 內(nèi)存分配器,每個(gè)線程有獨(dú)立的 threadata,通過(guò) threaddata 創(chuàng)建獨(dú)立的 allocator_。allocator_每次從 heap 申請(qǐng)一個(gè) page(比如中小對(duì)象是 256k),之后 page 在線程內(nèi)部分配內(nèi)存,我們具體看一下代碼。

內(nèi)存創(chuàng)建
在 GCApi.cpp 的 SafeAlloc 方法調(diào)用 mmap 創(chuàng)建虛擬內(nèi)存。
- 通過(guò) allocatedBytesCounter 保存分配內(nèi)存總量
- onMemoryAllocation 檢查是否需要觸發(fā) alloc gc
代碼塊:
void* SafeAlloc(uint64_t size)noexcept{
void* memory;
bool error;
if (compiler::disableMmap()) {
memory = calloc(size, 1);
error = memory == nullptr;
} else {
#if KONAN_WINDOWS
RuntimeFail("mmap is not available on mingw");
#elif KONAN_LINUX || KONAN_OHOS
memory = mmap(nullptr, size, PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ, MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE | MAP_POPULATE, -1, 0);
error = memory == MAP_FAILED;
#else
memory = mmap(nullptr, size, PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ, MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, -1, 0);
error = memory == MAP_FAILED;
#endif
}
if (error) {
konan::consoleErrorf("Out of memory trying to allocate %" PRIu64 "bytes: %s. Aborting.\n", size, strerror(errno));
std::abort();
}
auto previousSize = allocatedBytesCounter.fetch_add(static_cast<size_t>(size), std::memory_order_relaxed);
OnMemoryAllocation(previousSize + static_cast<size_t>(size));
return memory;
}onMemoryAllocation 通過(guò) HeapGrowthController 的 boundaryForHeapSize 方法來(lái)檢查 totalAllocatedBytes 是否觸發(fā) gc 閾值,我們后續(xù)分析。
代碼塊:
voidkotlin::OnMemoryAllocation(size_t totalAllocatedBytes)noexcept{
mm::GlobalData::Instance().gcScheduler().setAllocatedBytes(totalAllocatedBytes);
}
voidsetAllocatedBytes(size_t bytes)noexcept{
// Still checking allocations: with a long running loop all safepoints
// might be "met", so that's the only trigger to not run out of memory.
auto boundary = heapGrowthController_.boundaryForHeapSize(bytes);
switch (boundary) {
case HeapGrowthController::MemoryBoundary::kNone:
safePoint();
return;
case HeapGrowthController::MemoryBoundary::kTrigger:
RuntimeLogDebug({kTagGC}, "Scheduling GC by allocation");
scheduleGC_.scheduleNextEpochIfNotInProgress();
return;
case HeapGrowthController::MemoryBoundary::kTarget:
RuntimeLogDebug({kTagGC}, "Scheduling GC by allocation");
auto epoch = scheduleGC_.scheduleNextEpochIfNotInProgress();
RuntimeLogWarning({kTagGC}, "Pausing the mutators");
mutatorAssists_.requestAssists(epoch);
return;
}
}Custom 內(nèi)存分配器通過(guò) CreateObject 和 CreateArray 分配內(nèi)存。
- CreateObject 分配對(duì)象,如果類(typeInfo)加了 TF_HAS_FINALIZER 標(biāo)記,會(huì)通過(guò) extraObject 增加對(duì)象弱引用,gc 后調(diào)用 finialize 方法,后續(xù)分析
- CreateArray 分配 array
代碼塊:
ObjHeader* CustomAllocator::CreateObject(const TypeInfo* typeInfo)noexcept{
RuntimeAssert(!typeInfo->IsArray(), "Must not be an array");
auto descriptor = HeapObject::make_descriptor(typeInfo);
auto& heapObject = *descriptor.construct(Allocate(descriptor.size()));
ObjHeader* object = heapObject.header(descriptor).object();
if (typeInfo->flags_ & TF_HAS_FINALIZER) {
auto* extraObject = CreateExtraObject();
object->typeInfoOrMeta_ = reinterpret_cast<TypeInfo*>(new (extraObject) mm::ExtraObjectData(object, typeInfo));
} else {
object->typeInfoOrMeta_ = const_cast<TypeInfo*>(typeInfo);
}
return object;
}
ArrayHeader* CustomAllocator::CreateArray(const TypeInfo* typeInfo, uint32_t count)noexcept{
RuntimeAssert(typeInfo->IsArray(), "Must be an array");
auto descriptor = HeapArray::make_descriptor(typeInfo, count);
CustomAllocDebug("CustomAllocator@%p::CreateArray(%d), total size:%ld", this ,count, (long)descriptor.size());
auto& heapArray = *descriptor.construct(Allocate(descriptor.size()));
ArrayHeader* array = heapArray.header(descriptor).array();
array->typeInfoOrMeta_ = const_cast<TypeInfo*>(typeInfo);
array->count_ = count;
returnarray;
}對(duì)象大小通過(guò) HeapObject 計(jì)算,包括 ObjectData/ObjHeader/ObjectBody 三部分。
代碼塊:
structHeapObjHeader {
using descriptor = type_layout::Composite<HeapObjHeader, gc::GC::ObjectData, ObjHeader>;
structHeapObject {
using descriptor = type_layout::Composite<HeapObject, HeapObjHeader, ObjectBody>;Array 通過(guò) HeapArray 計(jì)算,包括 ObjectData, ArrayHeader, arrayBody。
代碼塊:
structHeapArrayHeader {
using descriptor = type_layout::Composite<HeapArrayHeader, gc::GC::ObjectData, ArrayHeader>;
// Header of value type array objects. Keep layout in sync with that of object header.
structArrayHeader {
TypeInfo* typeInfoOrMeta_;
// Elements count. Element size is stored in instanceSize_ field of TypeInfo, negated.
uint32_t count_;
};
structHeapArray {
using descriptor = type_layout::Composite<HeapArray, HeapArrayHeader, ArrayBody>;具體如下:

最后,通過(guò) Allocater 方法決定選用哪個(gè) page,我們后續(xù)分析下:
代碼塊:
uint8_t* CustomAllocator::Allocate(uint64_t size)noexcept{
RuntimeAssert(size, "CustomAllocator::Allocate cannot allocate 0 bytes");
//CustomAllocDebug("CustomAllocator::Allocate(%" PRIu64 ")", size);
uint64_t cellCount = (size + sizeof(Cell) - 1) / sizeof(Cell);
if (cellCount <= FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE) {
return AllocateInFixedBlockPage(cellCount);
} elseif (cellCount > NEXT_FIT_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE) {
return AllocateInSingleObjectPage(cellCount);
} else {
return AllocateInNextFitPage(cellCount);
}
}小對(duì)象分配
分配 8~1k 字節(jié)對(duì)象,MAX_BLOCK_SIZE = 128, 每次分配 cell 數(shù)量(一個(gè) cell 8 個(gè)字節(jié)) < 128 時(shí)會(huì)使用 FixedBlockPage 進(jìn)行內(nèi)存分配,每個(gè) page 默認(rèn) 256k。
代碼塊:
FixedBlockPage* FixedBlockPage::Create(uint32_t blockSize)noexcept{
CustomAllocInfo("FixedBlockPage::Create(%u)", blockSize);
RuntimeAssert(blockSize <= FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE, "blockSize too large for FixedBlockPage");
returnnew (SafeAlloc(FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_SIZE)) FixedBlockPage(blockSize);
}
inlineconstexprconstsize_t FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_SIZE = (256 * KiB);blockSize 是每個(gè) block 的大小,大小在 1~128 個(gè) cell。
代碼塊:
FixedBlockPage::FixedBlockPage(uint32_t blockSize) noexcept : blockSize_(blockSize) {
CustomAllocInfo("FixedBlockPage(%p)::FixedBlockPage(%u)", this, blockSize);
nextFree_.first = 0;
nextFree_.last = FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_CELL_COUNT / blockSize * blockSize;
end_ = FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_CELL_COUNT / blockSize * blockSize;
}TryAllocate 每次返回固定大小 cell,cell 數(shù)量取值 1~128。
代碼塊:
uint8_t* FixedBlockPage::TryAllocate() noexcept {
uint32_t next = nextFree_.first;
if (next < nextFree_.last) {
nextFree_.first += blockSize_;
return cells_[next].data;
}
if (next >= end_) return nullptr;
nextFree_ = cells_[next].nextFree;
memset(&cells_[next], 0, sizeof(cells_[next]));
return cells_[next].data;
}中對(duì)象分配
分配 1k~256k 對(duì)象,NextFitPage 和 FixedBlockPage 不同,同樣創(chuàng)建 256K 大小的內(nèi)存,每個(gè) page 可以分配不同 cell 數(shù)量的對(duì)象,而 FixedBlockPage 只能分配固定 cell 對(duì)象。
代碼塊:
NextFitPage* NextFitPage::Create(uint32_t cellCount) noexcept {
CustomAllocInfo("NextFitPage::Create(%u)", cellCount);
RuntimeAssert(cellCount < NEXT_FIT_PAGE_CELL_COUNT, "cellCount is too large for NextFitPage");
return new (SafeAlloc(NEXT_FIT_PAGE_SIZE)) NextFitPage(cellCount);
}
inline constexpr const size_t NEXT_FIT_PAGE_SIZE = (256 * KiB);cells 存放的是每個(gè) cell 編號(hào),從 0~cellCount - 1。
代碼塊:
NextFitPage::NextFitPage(uint32_t cellCount) noexcept : curBlock_(cells_) {
cells_[0] = Cell(0); // Size 0 ensures any actual use would break
cells_[1] = Cell(NEXT_FIT_PAGE_CELL_COUNT - 1);
}每次從 curBlock(cell)分配 blockSize, 如果不夠按照 blockSize 重新分配 cell。
代碼塊:
uint8_t* NextFitPage::TryAllocate(uint32_t blockSize)noexcept{
CustomAllocDebug("NextFitPage@%p::TryAllocate(%u)", this, blockSize);
// +1 accounts for header, since cell->size also includes header cell
uint32_t cellsNeeded = blockSize + 1;
uint8_t* block = curBlock_->TryAllocate(cellsNeeded);
if (block) return block;
UpdateCurBlock(cellsNeeded);
return curBlock_->TryAllocate(cellsNeeded);
}大對(duì)象分配
SingleObjectPage 每次只創(chuàng)建一個(gè)對(duì)象,大小為 objectSize,主要申請(qǐng)超過(guò) 256k 的大對(duì)象。
代碼塊:
SingleObjectPage* SingleObjectPage::Create(uint64_t cellCount)noexcept{
CustomAllocInfo("SingleObjectPage::Create(%" PRIu64 ")", cellCount);
RuntimeAssert(cellCount > NEXT_FIT_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE, "blockSize too small for SingleObjectPage");
uint64_t size = sizeof(SingleObjectPage) + cellCount * sizeof(uint64_t);
returnnew (SafeAlloc(size)) SingleObjectPage(size);
}Finalize 對(duì)象
不管哪種類型對(duì)象,如果需要 finalize,在 createObject 時(shí),通過(guò) ExtraObject 分配 24 字節(jié) ExtraObjectData 內(nèi)存。
ExtraObjectPage 分配 64k 內(nèi)存。
代碼塊:
ExtraObjectPage* ExtraObjectPage::Create(uint32_t ignored)noexcept{
CustomAllocInfo("ExtraObjectPage::Create()");
returnnew (SafeAlloc(EXTRA_OBJECT_PAGE_SIZE)) ExtraObjectPage();
}
// Optional data that's lazily allocated only for objects that need it.
classExtraObjectData :private Pinned {
private:
// Must be first to match `TypeInfo` layout.
const TypeInfo* typeInfo_;
std::atomic<uint32_t> flags_ = 0;
std::atomic<ObjHeader*> weakReferenceOrBaseObject_;nextFree 存放 cells 地址,創(chuàng)建 extraObjectCount 個(gè) cell。
代碼塊:
ExtraObjectPage::ExtraObjectPage() noexcept {
nextFree_.store(cells_, std::memory_order_relaxed);
ExtraObjectCell* end = cells_ + EXTRA_OBJECT_COUNT;
for (ExtraObjectCell* cell = cells_; cell < end; cell = cell->next_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed)) {
cell->next_.store(cell + 1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
}TryAllocate 每次分配一個(gè) cell。
代碼塊:
mm::ExtraObjectData* ExtraObjectPage::TryAllocate()noexcept{
auto* next = nextFree_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
if (next >= cells_ + EXTRA_OBJECT_COUNT) {
returnnullptr;
}
ExtraObjectCell* freeBlock = next;
nextFree_.store(freeBlock->next_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed), std::memory_order_relaxed);
CustomAllocDebug("ExtraObjectPage(%p)::TryAllocate() = %p", this, freeBlock->Data());
return freeBlock->Data();
}FinalizerQueue 用于存放 finialze 對(duì)象,gc 后會(huì)遍歷 FinalizerQueue,調(diào)用對(duì)象 finialize 方法。
代碼塊:
classCustomAllocator {
private:
uint8_t* Allocate(uint64_t cellCount)noexcept;
uint8_t* AllocateInSingleObjectPage(uint64_t cellCount)noexcept;
uint8_t* AllocateInNextFitPage(uint32_t cellCount)noexcept;
uint8_t* AllocateInFixedBlockPage(uint32_t cellCount)noexcept;
Heap& heap_;
NextFitPage* nextFitPage_;
FixedBlockPage* fixedBlockPages_[FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE + 1];
ExtraObjectPage* extraObjectPage_;
FinalizerQueue finalizerQueue_;總結(jié)一下,custom 內(nèi)存分配器一共有四種內(nèi)存分配方式,F(xiàn)ixedBlockPage/NextFitPage 適用于中小對(duì)象,SingleObjecPage 適用于大對(duì)象,ExtraObjectPage 適用于需要 finalize 對(duì)象的額外數(shù)據(jù)。
如下是簡(jiǎn)單總結(jié):

上面分析的 FixedBlockPage/SingleObjectPage/NextFitPage 都定義了 Sweep 方法,用于 GC 時(shí)回收內(nèi)存,不同的 GC 算法都會(huì)調(diào)用同樣的 sweep 方法,我們繼續(xù)看一下 GC。
GC
GC 有三種類型,默認(rèn) pcms,cms 需要手動(dòng)配置。
- cms 是并發(fā)標(biāo)記的,只在遍歷 gc root 時(shí)暫停線程,性能最好
- stms,需要 stop world 暫停線程,性能很差
- 默認(rèn) pcms 可以支持多線程 gc,也會(huì) stop the world 暫停線程
stms 是早期的垃圾回收器,cms 是最新的,我們從代碼層面分別看下。
stms
GCImpl.cpp 是 GC 實(shí)現(xiàn)的接口類,每個(gè) GC 垃圾回收器都需要實(shí)現(xiàn)一下,包括幾個(gè)部分:
- SameThreadMarkAndSweep gc_,GC 整體都是由 SameThreadMarkAndSweep 完成的
- gcScheduler 調(diào)度策略,gcScheduler 后續(xù)會(huì)分析
代碼塊:
classGC::Impl : private Pinned {
public:
explicitImpl(alloc::Allocator& allocator, gcScheduler::GCScheduler& gcScheduler)noexcept : gc_(allocator, gcScheduler){}
SameThreadMarkAndSweep& gc()noexcept{ return gc_; }
private:
SameThreadMarkAndSweep gc_;
};SameThreadMarkAndSweep 在構(gòu)造函數(shù)中創(chuàng)建 GC thread 線程,并通過(guò) state_。waitScheduled 判斷是否調(diào)用 PerformFullGC,這里用了 do/while 循環(huán),state_是 GCStateHolder 變量。
代碼塊:
gc::SameThreadMarkAndSweep::SameThreadMarkAndSweep(alloc::Allocator& allocator, gcScheduler::GCScheduler& gcScheduler) noexcept :
allocator_(allocator), gcScheduler_(gcScheduler), finalizerProcessor_([this](int64_t epoch) noexcept {
GCHandle::getByEpoch(epoch).finalizersDone();
state_.finalized(epoch);
}) {
gcThread_ = ScopedThread(ScopedThread::attributes().name("GC thread"), [this] {
while (true) {
auto epoch = state_.waitScheduled();
if (epoch.has_value()) {
PerformFullGC(*epoch);
} else {
break;
}
}
});
}PerformFullGC 主要做幾個(gè)事情:
- StopTheWord 所有線程將線程暫停執(zhí)行
- collectRootSet 收集 gc root
- Mark 會(huì)根據(jù) gc root 標(biāo)記存活對(duì)象
- processWeaks 處理 weakReference
- prepareForGC 通知每個(gè)線程 customallocator 去掉 page 引用,為存活對(duì)象 sweep 提前做準(zhǔn)備
- heap.Sweep 釋放非存活對(duì)象
- resumeTheWorld 喚醒線程
- finalizerProcessor 調(diào)用對(duì)象 finialize 方法,之前會(huì)收集所有線程的 finalize 對(duì)象
代碼塊:
void gc::SameThreadMarkAndSweep::PerformFullGC(int64_t epoch) noexcept {
stopTheWorld(gcHandle, "GC stop the world");
gc::collectRootSet<internal::MarkTraits>(gcHandle, markQueue_, [](mm::ThreadData&) { returntrue; });
gc::Mark<internal::MarkTraits>(gcHandle, markQueue_);
gc::processWeaks<DefaultProcessWeaksTraits>(gcHandle, mm::SpecialRefRegistry::instance());
// This should really be done by each individual thread while waiting
int threadCount = 0;
for (auto& thread : kotlin::mm::ThreadRegistry::Instance().LockForIter()) {
thread.allocator().prepareForGC();
++threadCount;
}
allocator_.prepareForGC();
// also sweeps extraObjects
auto finalizerQueue = allocator_.impl().heap().Sweep(gcHandle);
for (auto& thread : kotlin::mm::ThreadRegistry::Instance().LockForIter()) {
finalizerQueue.mergeFrom(thread.allocator().impl().alloc().ExtractFinalizerQueue());
}
finalizerQueue.mergeFrom(allocator_.impl().heap().ExtractFinalizerQueue());
resumeTheWorld(gcHandle);
finalizerProcessor_.ScheduleTasks(std::move(finalizerQueue.regular), epoch);
mainThreadFinalizerProcessor_.schedule(std::move(finalizerQueue.mainThread), epoch);
}具體流程如圖:

collectRootSet 通過(guò) collectRootSetForThread 從線程 stack/tls gc root, collectRootSetGlobals 讀取 static 和 jni 調(diào)用的 gc root,最終放到 markQueue。

代碼塊:
// TODO: This needs some tests now.
template <typename Traits, typename F>
voidcollectRootSet(GCHandle handle, typename Traits::MarkQueue& markQueue, F&& filter)noexcept{
Traits::clear(markQueue);
for (auto& thread : mm::GlobalData::Instance().threadRegistry().LockForIter()) {
if (!filter(thread))
continue;
thread.Publish();
collectRootSetForThread<Traits>(handle, markQueue, thread);
}
collectRootSetGlobals<Traits>(handle, markQueue);
}Mark 方法會(huì)從 markQueue 中取出存活對(duì)象,然后調(diào)用 processInMark 處理成員變量。
代碼塊:
template <typename Traits>
voidMark(GCHandle::GCMarkScope& markHandle, typename Traits::MarkQueue& markQueue)noexcept{
while (ObjHeader* top = Traits::tryDequeue(markQueue)) {
markHandle.addObject();
Traits::processInMark(markQueue, top);
// TODO: Consider moving it before processInMark to make the latter something of a tail call.
if (auto* extraObjectData = mm::ExtraObjectData::Get(top)) {
internal::processExtraObjectData<Traits>(markHandle, markQueue, *extraObjectData, top);
}
}
}和 android 不同,kmp 會(huì)通過(guò)靜態(tài)代碼分析判斷對(duì)象在棧上還是堆上分配。
棧上分配的對(duì)象在方法調(diào)用結(jié)束后可以返回,通過(guò) field->heap 判斷變量在堆上還是棧上,棧上的對(duì)象不需要放到 markQueue。
代碼塊:
template <typename Traits>
voidprocessFieldInMark(void* state, ObjHeader* object, ObjHeader* field)noexcept{
auto& markQueue = *static_cast<typename Traits::MarkQueue*>(state);
if (field->heap()) {
Traits::tryEnqueue(markQueue, field);
}
ifconstexpr(!Traits::kAllowHeapToStackRefs){
if (object->heap()) {
RuntimeAssert(!field->local(), "Heap object %p references stack object %p[typeInfo=%p]", object, field, field->type_info());
}
}
}tryEnqueue 將對(duì)象的 ObjectData(上面分析過(guò),在每個(gè)對(duì)象開頭 8 個(gè)字節(jié)),通過(guò) tryPush 放到 queue 里面。
代碼塊:
static ALWAYS_INLINE booltryEnqueue(AnyQueue& queue, ObjHeader* object)noexcept{
auto& objectData = alloc::objectDataForObject(object);
bool pushed = queue.tryPush(objectData);
return pushed;
}這里 queue 實(shí)現(xiàn)上是一個(gè)鏈表,每個(gè)元素是 ObjectData 中的 next_變量,如果對(duì)象 next_有值,說(shuō)明已經(jīng) mark 過(guò),直接返回。sweep 時(shí)判斷 next_有值就不會(huì)釋放對(duì)象。
代碼塊:
std::optional<iterator> try_insert_after(iterator pos, reference value) noexcept {
RuntimeAssert(pos != end(), "Attempted to try_insert_after end()");
RuntimeAssert(pos != iterator(), "Attempted to try_insert_after empty iterator");
if (!trySetNext(&value, next(pos.node_))) {
return std::nullopt;
}
setNext(pos.node_, &value);
return iterator(&value);
}
void setNext(ObjectData* next) noexcept {
RuntimeAssert(next, "next cannot be nullptr");
next_.store(next, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
bool trySetNext(ObjectData* next) noexcept {
RuntimeAssert(next, "next cannot be nullptr");
ObjectData* expected = nullptr;
return next_.compare_exchange_strong(expected, next, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}具體邏輯如下:

從代碼看,stms 代碼邏輯非常完整,但是 stw 會(huì)造成線程暫停,影響性能,pmcs 和 stms 實(shí)現(xiàn)差不多。
我們繼續(xù)看下 cms 如何去掉 stop the world。
cms
從代碼看,cms 在遍歷 gc root 時(shí)才會(huì) stop the world,主要實(shí)現(xiàn)在 markDispatcher_。runMainInSTW。
代碼塊:
void gc::ConcurrentMarkAndSweep::PerformFullGC(int64_t epoch) noexcept {
std::unique_lock mainGCLock(gcMutex);
auto gcHandle = GCHandle::create(epoch);
stopTheWorld(gcHandle, "GC stop the world #1: collect root set");
auto& scheduler = gcScheduler_;
scheduler.onGCStart();
state_.start(epoch);
markDispatcher_.runMainInSTW();在 completeMutatorSRootSet 獲取到 gc root 后,通過(guò) resumeTheWorld 喚醒線程,這樣后續(xù) Mark 階段就不會(huì)暫停線程了。在 Mark 階段新產(chǎn)生的對(duì)象都是存活對(duì)象。
代碼塊:
void gc::mark::ConcurrentMark::runMainInSTW() {
ParallelProcessor::Worker mainWorker(*parallelProcessor_);
// create mutator mark queues
for (auto& thread : *lockedMutatorsList_) {
thread.gc().impl().gc().mark().markQueue().construct(*parallelProcessor_);
}
completeMutatorsRootSet(mainWorker);
// global root set must be collected after all the mutator's global data have been published
collectRootSetGlobals<MarkTraits>(gcHandle(), mainWorker);
barriers::enableBarriers(gcHandle().getEpoch());
resumeTheWorld(gcHandle());具體流程圖:

GCScheduler
默認(rèn)是 adaptive 模式,通過(guò) GC timer thread 線程在應(yīng)用處于前臺(tái)時(shí)定時(shí)觸發(fā) GC, config_。regularGcInterval 指定,默認(rèn) 10s。
代碼塊:
classGCSchedulerDataAdaptive{
public:
GCSchedulerDataAdaptive(GCSchedulerConfig& config, std::function<int64_t()> scheduleGC) noexcept :
config_(config),
scheduleGC_(std::move(scheduleGC)),
appStateTracking_(mm::GlobalData::Instance().appStateTracking()),
heapGrowthController_(config),
regularIntervalPacer_(config),
timer_("GC Timer thread", config_.regularGcInterval(), [this] {
if (appStateTracking_.state() == mm::AppStateTracking::State::kBackground) {
return;
}
if (regularIntervalPacer_.NeedsGC()) {
RuntimeLogDebug({kTagGC}, "Scheduling GC by timer");
scheduleGC_.scheduleNextEpochIfNotInProgress();
}
}) {
}也可以在 alloc 對(duì)象時(shí)觸發(fā),boundaryForHeapSize 返回 kTrigger 觸發(fā) gc,內(nèi)存分配的時(shí)候 safealloc 通過(guò) mmap 分配內(nèi)存后會(huì)調(diào)用 setAllocatedBytes 判斷是否需要 gc。
代碼塊:
voidsetAllocatedBytes(size_t bytes)noexcept{
auto boundary = heapGrowthController_.boundaryForHeapSize(bytes);
switch (boundary) {
case HeapGrowthController::MemoryBoundary::kNone:
return;
case HeapGrowthController::MemoryBoundary::kTrigger:
scheduleGC_.scheduleNextEpochIfNotInProgress();
return;
case HeapGrowthController::MemoryBoundary::kTarget:
mutatorAssists_.requestAssists(epoch);
return;
}
}判斷條件是已分配內(nèi)存 totalAllocatedBytes >= targetHeapBytes(默認(rèn) 10M)。
代碼塊:
// Can be called by any thread.
MemoryBoundary boundaryForHeapSize(size_t totalAllocatedBytes)noexcept{
if (totalAllocatedBytes >= targetHeapBytes_) {
return config_.mutatorAssists() ? MemoryBoundary::kTarget : MemoryBoundary::kTrigger;
} elseif (totalAllocatedBytes >= triggerHeapBytes_) {
return MemoryBoundary::kTrigger;
} else {
return MemoryBoundary::kNone;
}
}每次 gc 后,通過(guò) updateboundaries 重新計(jì)算 targetHeapBytes,涉及 heapTriggerCoefficient(默認(rèn) 0.9), targetheapUtilization(默認(rèn) 0.1),都可以調(diào)整優(yōu)化。
代碼塊:
// Called by the GC thread.
voidupdateBoundaries(size_t aliveBytes)noexcept{
if (config_.autoTune.load()) {
double targetHeapBytes = static_cast<double>(aliveBytes) / config_.targetHeapUtilization;
if (!std::isfinite(targetHeapBytes)) {
// This shouldn't happen in practice: targetHeapUtilization is in (0, 1]. But in case it does, don't touch anything.
return;
}
double minHeapBytes = static_cast<double>(config_.minHeapBytes.load(std::memory_order_relaxed));
double maxHeapBytes = static_cast<double>(config_.maxHeapBytes.load(std::memory_order_relaxed));
targetHeapBytes = std::min(std::max(targetHeapBytes, minHeapBytes), maxHeapBytes);
triggerHeapBytes_ = static_cast<size_t>(targetHeapBytes * config_.heapTriggerCoefficient.load(std::memory_order_relaxed));
config_.targetHeapBytes.store(static_cast<int64_t>(targetHeapBytes), std::memory_order_relaxed);
targetHeapBytes_ = static_cast<size_t>(targetHeapBytes);
} else {
targetHeapBytes_ = config_.targetHeapBytes.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
}aggressive 模式只會(huì)觸發(fā) alloc gc,不會(huì)定時(shí)觸發(fā)。
目前問(wèn)題總結(jié)
- std 內(nèi)存分配器占用內(nèi)存很少,但是實(shí)踐發(fā)現(xiàn)切換后會(huì)頻繁的 alloc gc,性能比 custom 差很多
- cms 在 mark 階段不會(huì)暫停線程,性能更好,但是默認(rèn)是 pmcs
- GcScheduler 默認(rèn) adaptive 模式,會(huì)有定時(shí)觸發(fā) GC(默認(rèn) 10s)以及默認(rèn) heap(10M)導(dǎo)致頻繁 gc
- gc 不支持分代,每次遍歷所有對(duì)象比較耗時(shí)
- custom 內(nèi)存分配器每個(gè)線程內(nèi)存分配是獨(dú)立的,相當(dāng)于 android 的 tlab。不過(guò)實(shí)踐發(fā)現(xiàn)物理內(nèi)存很容易 200M+,原因是沒(méi)有做內(nèi)存碎片整理,需要我們自己實(shí)現(xiàn)
針對(duì)這幾個(gè)問(wèn)題,我們做了優(yōu)化并在抖音落地。
優(yōu)化落地
heap 配置優(yōu)化
從 updateBoundaries 分析看,影響下次 gc 主要是 targeHeapBytes,而 targeHeapBytes 默認(rèn) 10M,heapTriggerCoefficient * 10 = 9M 時(shí)就會(huì)觸發(fā) GC,GC 后 targeHeapBytes = 存活對(duì)象大小 / targetHeapUtilization(0.5)。
代碼塊:
std::atomic<int64_t> regularGcIntervalMicroseconds = 10 * 1000 * 1000;
// GC will try to keep object bytes under this amount. If object bytes have
// become bigger than this value, and `mutatorAssists` are enabled the GC will
// stop the world and wait until current epoch finishes.
// Adapts after each GC epoch when `autoTune = true`.
std::atomic<int64_t> targetHeapBytes = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
// The rate at which `targetHeapBytes` changes when `autoTune = true`. Concretely: if after the collection
// `N` object bytes remain in the heap, the next `targetHeapBytes` will be `N / targetHeapUtilization` capped
// between `minHeapBytes` and `maxHeapBytes`.
std::atomic<double> targetHeapUtilization = 0.5;
// GC will be triggered when object bytes reach `heapTriggerCoefficient * targetHeapBytes`.
std::atomic<double> heapTriggerCoefficient = 0.9;從實(shí)際看,alloc gc 觸發(fā)次數(shù)比較多,可以設(shè)置這幾個(gè)變量,另外滑動(dòng)時(shí) regularGcIntervalMicrosecnotallow=10s 定時(shí) gc 也會(huì)占用 cpu,可以先在滑動(dòng)時(shí)增大,后續(xù)根據(jù) heap 大小來(lái)觸發(fā)。
以頭條關(guān)注頁(yè)為例,默認(rèn)內(nèi)存參數(shù)在滑動(dòng)的時(shí)候會(huì)頻繁觸發(fā) gc,導(dǎo)致幀率降低。

默認(rèn)參數(shù)滑動(dòng)時(shí) gc 間隔只有 200ms 左右
在業(yè)務(wù)層可以通過(guò) kotlin.native.runtime.GC 屬性來(lái)直接調(diào)整調(diào)整參數(shù)。

調(diào)大 gc 閾值內(nèi)存

調(diào)整之后滑動(dòng)間隔為默認(rèn)的 10s
滑動(dòng) gc 抑制
目前 kotlin-native 的 gc 機(jī)制會(huì)定時(shí) gc,如果恰好是在滑動(dòng)的時(shí)候觸發(fā) gc,就可能會(huì)導(dǎo)致卡頓,因此需要在滑動(dòng)的時(shí)候讓 runtime 不進(jìn)行 gc。方法是滑動(dòng)時(shí)候通過(guò)GC.regularGCInterval來(lái)調(diào)整 gc 間隔到一個(gè)相對(duì)長(zhǎng)的值,比如 1 分鐘,等到滑動(dòng)結(jié)束的時(shí)候再還原回去。
gc 配置優(yōu)化
默認(rèn)是 pmcs,可以改成 cms,減少線程暫停時(shí)間,在大多數(shù)情況下 gmcs 線程暫停(STW)時(shí)間 5ms 左右,如果想要不掉幀,一幀的渲染時(shí)間為 8.33ms(120fps),留給處理業(yè)務(wù)的時(shí)間只有 3ms,實(shí)測(cè)下來(lái)滑動(dòng)帶圖場(chǎng)景基本穩(wěn)定掉幀。cms 的線程暫停(STW)時(shí)間為 0.2ms 左右。直接降低了一個(gè)數(shù)量級(jí)。

默認(rèn) gmcs gc 時(shí)的暫停時(shí)間

改為 cms 時(shí),gc 的暫停時(shí)間
經(jīng)過(guò)測(cè)試,上述三項(xiàng)優(yōu)化上了之后,頭條個(gè)人頁(yè)滑動(dòng)場(chǎng)景的幀率可從 110fps 提升到 117fps。
內(nèi)存碎片優(yōu)化
- 調(diào)整 FixedBlockPage 數(shù)量,cell size,每個(gè)線程都有獨(dú)立的 fixedBlockPages 數(shù)組,大小為 256k * 128 = 32M,gc 后由于沒(méi)有內(nèi)存碎片整理,內(nèi)存空洞較大。目前將 FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_SIZE 設(shè)置為 64k,FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE 設(shè)置為 16,一個(gè)線程占用 1M。
代碼塊:
classCustomAllocator {
private:
Heap& heap_;
NextFitPage* nextFitPage_;
FixedBlockPage* fixedBlockPages_[FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE + 1];
ExtraObjectPage* extraObjectPage_;
FinalizerQueue finalizerQueue_;
inlineconstexprconstsize_t FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_SIZE = (256 * KiB);
inlineconstexprconstint FIXED_BLOCK_PAGE_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE = 128;- 按頁(yè)釋放空洞內(nèi)存
Sweep 時(shí)如果內(nèi)存需要釋放,只是 memset 將內(nèi)存設(shè)置為 0,并不會(huì)釋放內(nèi)存。
代碼塊:
boolFixedBlockPage::Sweep(GCSweepScope& sweepHandle, FinalizerQueue& finalizerQueue)noexcept{
for (uint32_t cell = 0 ; cell < end_ ; cell += blockSize_) {
// Go through the occupied cells.
for (; cell < nextFree.first ; cell += blockSize_) {
if (!SweepObject(cells_[cell].data, finalizerQueue, sweepHandle)) {
// We should null this cell out, but we will do so in batch later.
continue;
}
if (prevLive + blockSize_ < cell) {
// We found an alive cell that ended a run of swept cells or a known unoccupied range.
uint32_t prevCell = cell - blockSize_;
// Nulling in batch.
memset(&cells_[prevLive + blockSize_], 0, (prevCell - prevLive) * sizeof(FixedBlockCell));
}
}將 memset 改成 madvise 按頁(yè)釋放內(nèi)存。
代碼塊:
#ifndef KONAN_WINDOWS
staticsize_t kPageSize = sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE);
#endif
voidZeroAndReleasePages(void* address, size_t length)noexcept{
#ifdef KONAN_WINDOWS
#else
if (length <= 0) {
return;
}
uint8_t* const mem_begin = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(address);
uint8_t* const mem_end = mem_begin + length;
uint8_t* const page_begin = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(RoundUp(reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(mem_begin), kPageSize));
uint8_t* const page_end = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(RoundDown(reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(mem_end), kPageSize));
if (page_begin >= page_end) {
// No possible area to madvise.
} else {
madvise(page_begin, page_end - page_begin, MADV_DONTNEED);
}
#endif
}
//#endif經(jīng)測(cè)試,在頭條關(guān)注頁(yè)長(zhǎng)時(shí)間滑動(dòng)情況下,內(nèi)存碎片優(yōu)化 -200M 內(nèi)存。
- mmap 去掉 MAP_POPULATE 標(biāo)記
Runtime 使用 mmap 進(jìn)行 Page 分配,如下:
代碼塊:
void* SafeAlloc(uint64_t size)noexcept{
//......
#if KONAN_WINDOWS
RuntimeFail("mmap is not available on mingw");
#elif KONAN_LINUX
memory = mmap(nullptr, size, PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ, MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE | MAP_POPULATE, -1, 0);
error = memory == MAP_FAILED;
//......
}調(diào)用的參數(shù)有一個(gè) MAP_POPULATE 標(biāo)記,它的主要作用是預(yù)先填充(prefault)映射區(qū)域的頁(yè)表。
在標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的 mmap 調(diào)用中,系統(tǒng)僅會(huì)在進(jìn)程的虛擬內(nèi)存空間中分配一段虛擬內(nèi)存區(qū)域,并建立虛擬地址與文件(或匿名內(nèi)存)之間的映射關(guān)系,但并不會(huì)立即分配物理內(nèi)存。物理內(nèi)存的實(shí)際分配會(huì)延遲到 CPU 首次訪問(wèn)這段虛擬內(nèi)存時(shí),通過(guò)缺頁(yè)中斷(page fault)機(jī)制觸發(fā)。
而當(dāng)使用 MAP_POPULATE 標(biāo)志時(shí),系統(tǒng)會(huì)在 mmap 調(diào)用期間就預(yù)先填充頁(yè)表,對(duì)于文件映射,還會(huì)觸發(fā)對(duì)文件的預(yù)讀(read-ahead)操作,去掉該標(biāo)記能減少物理內(nèi)存占用。
vma 重用優(yōu)化
CMS GC 在 sweep 時(shí)會(huì)將 empty page 收集起來(lái):
代碼塊:
T* SweepSingle(GCSweepScope& sweepHandle, T* page, AtomicStack<T>& from, AtomicStack<T>& to, FinalizerQueue& finalizerQueue)noexcept{
if (!page) {
returnnullptr;
}
do {
if (page->Sweep(sweepHandle, finalizerQueue)) {
to.Push(page);
return page;
}
empty_.Push(page);
} while ((page = from.Pop()));
returnnullptr;
}在下次 GC 的第二次 STW 時(shí),將 empty page 通過(guò) munmap 釋放物理內(nèi)存:
代碼塊:
void PrepareForGC() noexcept {
unswept_.TransferAllFrom(std::move(ready_));
unswept_.TransferAllFrom(std::move(used_));
T* page;
// Destory 使用 munmap 釋放 vma
while ((page = empty_.Pop())) page->Destroy();
}但在 empty 比較多的場(chǎng)景下,這樣會(huì)導(dǎo)致 STW 的時(shí)間顯著變長(zhǎng),影響程序性能。
因此,我們做了 vma 重用的優(yōu)化,在收集 empty page 時(shí),對(duì)其使用 madvise (MADV_DONTNEED) 來(lái)釋放物理內(nèi)存 ,極大降低了第二次 STW 的時(shí)間。
gc 分代
在 sweep 調(diào)用 ObjectData tryResetMark 時(shí),如果是 sticky(young),就標(biāo)記成 kStickMark,這樣下次 gc 時(shí)發(fā)現(xiàn)對(duì)象還是 mark 狀態(tài),就不會(huì)釋放,也不會(huì)添加到 markqueue。
代碼塊:
booltryResetMark()noexcept{
if (!isSticky) {
unMarkSticky();
}
if (next() == nullptr) returnfalse;
markUncontendedSticky();
markSticky();
returntrue;
}
voidmarkSticky()noexcept{
auto nextVal = reinterpret_cast<ObjectData*>(kStickyMark);
next_.store(nextVal, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
boolunMarkSticky(){
auto expected = reinterpret_cast<ObjectData*>(kStickyMark);
return next_.compare_exchange_strong(expected, nullptr, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}在不是 sticky 模式下,tryEnqueue 時(shí),unMarkSticky 取消重新標(biāo)記。
代碼塊:
static ALWAYS_INLINE booltryEnqueue(AnyQueue& queue, ObjHeader* object)noexcept{
auto& objectData = alloc::objectDataForObject(object);
if (!GC::ObjectData::isSticky) {
objectData.unMarkSticky();
}
bool pushed = queue.tryPush(objectData);
return pushed;
}gc 分代不會(huì)減少 gc 暫停線程時(shí)間,可以減少 gc 線程整體耗時(shí) 10m~30ms,但是由于內(nèi)存釋放不及時(shí)也會(huì)造成內(nèi)存占用過(guò)大。
對(duì)象逃逸分析
通過(guò)靜態(tài)代碼分析變量在堆上還是棧上分配,在棧上分配對(duì)象在函數(shù)調(diào)用結(jié)束后可以立即釋放。測(cè)試發(fā)現(xiàn),棧上對(duì)象數(shù)量/堆上對(duì)象數(shù)量 = 1/8,業(yè)務(wù)盡量增加棧上對(duì)象數(shù)量。
- 盡量少用類成員變量,在方法內(nèi)部分配變量
- 少用多態(tài),增加識(shí)別成棧上對(duì)象概率
內(nèi)存碎片整理
由于棧上變量不會(huì)調(diào)用一次 loadslot 更新為新對(duì)象地址,還有兩個(gè)問(wèn)題需要解決。
- 內(nèi)存碎片整理是 stw
- 不會(huì)整理?xiàng)I弦米兞?/span>
如下是部分實(shí)現(xiàn),判斷 copied,從老對(duì)象 object 中取出新對(duì)象地址,否則就用 memcpy 進(jìn)行 copy。
代碼塊:
if (gc::isCopied(object)) {
UpdateStackRef(newObjAddr, gc::copyObj(object));
return;
}
//cas多線程狀態(tài)設(shè)置開始狀態(tài)
if (!gc::isCopying(object)) {
gc::trySetCopyObj(object, reinterpret_cast<ObjHeader*>(gc::kObjectCopy));
} else {
//否則等待copy完成
while (gc::isCopying(object)) {};
if (gc::isCopied(object)) {
UpdateStackRef(newObjAddr, gc::copyObj(object));
}
return;
}
newObj = threadData->allocator().allocateObject(typeInfo);
// Prevents unsafe class publication (see KT-58995).
// Also important in case of the concurrent GC mark phase.
std::atomic_thread_fence(std::memory_order_release);
size = computeObjectSize(typeInfo);
std::memcpy(reinterpret_cast<int8_t *>(newObj) + sizeof(ObjHeader), reinterpret_cast<int8_t *>(object) + sizeof(ObjHeader),
size - sizeof(ObjHeader));
gc::trySetCopyObj(object, newObj);
UpdateStackRef(newObjAddr, newObj);抖音線上實(shí)驗(yàn)有 10%內(nèi)存優(yōu)化。
未來(lái)規(guī)劃
- 內(nèi)存碎片整理使用 llvm stackmap,gc 時(shí)線程從 stw 改成 concurrent
- 指針壓縮,將對(duì)象中的成員變量以及數(shù)組元素指針從 64 位改為 32 位,可以優(yōu)化 10%+內(nèi)存
- 大對(duì)象和小對(duì)象在同一個(gè) heap,可以放到不同的 heap,減少 gc 次數(shù)。