BufferedInputStream類方法,使用BufferedInputStream類讀取文本文件內(nèi)容
大家好,我是Java進階者。
前言
本文主要學習BufferedInputStream類方法,使用BufferedInputStream類讀取文本文件內(nèi)容、BufferedOutputStream類向文件中寫入內(nèi)容和它的常用方法,接下來小編帶大家一起來學習!
一、BufferedInputStream類方法
1.BufferedInputStream是緩沖輸入流,可以減少訪問磁盤的次數(shù),提高文件的讀取性能,它是FilterInputStream類的子類。
2.BufferedInputStream類方法有:
(1)int available()方法:用于返回輸入流中可用的未讀字節(jié)數(shù),而不會由于下一次為此InputStream的方法的調(diào)用而阻塞。
(2)void close()方法:關(guān)閉此輸入流并釋放與該流關(guān)聯(lián)的所有系統(tǒng)資源。
(3)void mark(int readlimit)方法:輸入流的當前位置做個標記,readlimit參數(shù)是輸入流在標記位置失效前允許讀取的字節(jié)數(shù)。
(4)boolean markSupported()方法:測試輸入流是否支持mark和reset方法。
(5)int read()方法:讀取一個字節(jié)。
(6)int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法:讀取多個字節(jié)到字節(jié)數(shù)組b中,參數(shù)off是數(shù)組偏移量,參數(shù)len是讀取數(shù)據(jù)的長度。
(7)void reset()方法:重置流的當前位置到前面標記的位置。
(8)long skip(long n)方法:略過流中的數(shù)據(jù)。若數(shù)據(jù)不夠時,跳過僅有的字節(jié),返回跳過的字節(jié)數(shù)。
二、BufferedInputStream類read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法
1.public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法:讀取多個字節(jié)到字節(jié)數(shù)組b中,參數(shù)off是數(shù)組偏移量,參數(shù)len是讀取數(shù)據(jù)的長度。
2.read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法例子的實現(xiàn):
(1)在text文件夾下創(chuàng)建一個test.txt文件并寫入"helloworld,java!"內(nèi)容。
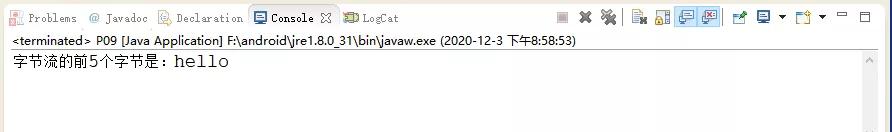
(2)建立輸入流BufferedInputStream, 緩沖區(qū)大小為8,讀取字節(jié)流的前5個字節(jié)的代碼的實現(xiàn)。
- public class P09 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- //創(chuàng)建一個帶有緩沖區(qū)的輸入流
- BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("text/test"), 8);
- //從字節(jié)流中讀取5個字節(jié)
- byte temp[]=new byte[5];
- //read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法
- in.read(temp,0,5);
- System.out.println("字節(jié)流的前5個字節(jié)是:"+new String(temp));
- }
- }
運行的結(jié)果如下圖所示:
三、BufferedInputStream類mark()和reset()方法
1.void mark(int readlimit)方法:輸入流的當前位置做個標記,readlimit參數(shù)是輸入流在標記位置失效前允許讀取的字節(jié)數(shù)。
2.void reset()方法:重置流的當前位置到前面標記的位置。
3.例子的實現(xiàn):
- import java.io.*;
- public class P09 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- //創(chuàng)建一個帶有緩沖區(qū)的輸入流
- BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("text/test"), 8);
- //從字節(jié)流中讀取5個字節(jié)
- byte temp[]=new byte[5];
- //read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法
- in.read(temp,0,5);
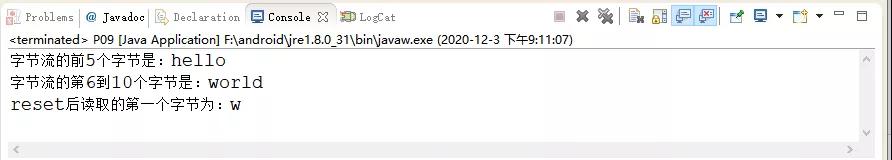
- System.out.println("字節(jié)流的前5個字節(jié)是:"+new String(temp));
- //標記測試
- in.mark(6);
- in.read(temp,0,5);
- System.out.println("字節(jié)流的第6到10個字節(jié)是:"+new String(temp));
- //reset()方法
- in.reset();
- System.out.printf("reset后讀取的第一個字節(jié)為:%c", in.read());
- }
- }
運行的結(jié)果如下圖所示:
四、BufferedOutputStream類
1.BufferedOutputStream類是字節(jié)緩沖輸出流,它是FilterOutputStream類的子類。
2.BufferedOutputStream類常用的方法有以下所示:
(1)void write(int b)方法:一次寫一個字節(jié)。
(2)void write(byte[] b,int off,int len)方法:從指定數(shù)組b中的從偏移量off開始len個字節(jié)寫入文件輸出流中。off參數(shù)表示數(shù)組偏移量,len表示要寫入的字節(jié)數(shù)。
(3)void flush()方法:刷新此緩沖的輸出流。這迫使所有緩沖的輸出字節(jié)被寫出到底層輸出流中。
(4)void close()方法:關(guān)閉此輸入流并釋放與該流關(guān)聯(lián)的所有系統(tǒng)資源。
3.BufferedOutputStream方法的實現(xiàn)例子:
- import java.io.*;
- public class P10 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- //創(chuàng)建一個帶緩沖流的輸出流
- BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("text/test10"));
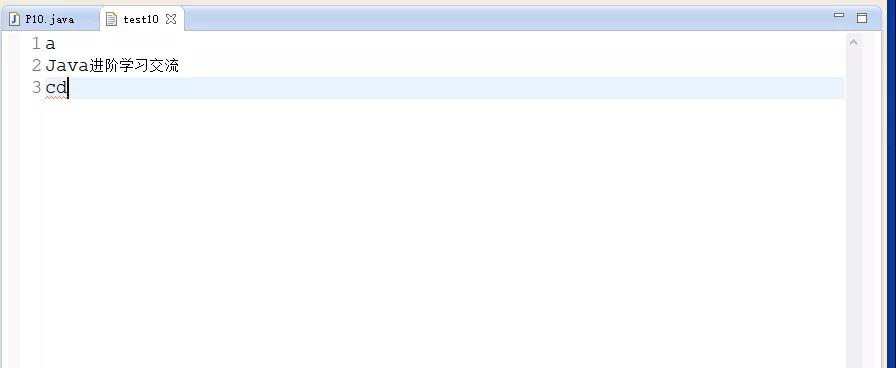
- //在文本文件中寫入小寫a字母
- bos.write(97);
- //在文本文件中寫入"Java進階學習交流"
- bos.write("\nJava進階學習交流\n".getBytes());
- //創(chuàng)建一個字節(jié)數(shù)組
- byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,100,101};
- //從偏移量2位置開始就是c,獲取寫入2個字節(jié)數(shù)
- bos.write(bytes,2,2);
- //刷新緩沖流
- bos.flush();
- //關(guān)閉流
- bos.close();
- }
- }
運行的結(jié)果如下所示:
五、總結(jié)
本文主要介紹了BufferedInputStream類方法、BufferedOutputStream類。介紹了BufferedInputStream的read(byte[] b, int off, int len)方法、mark()和reset()方法通過例子理解這些方法用法,使用BufferedInputStream來讀取文本的內(nèi)容。BufferedOutputStream類是字節(jié)緩沖輸出流,它是FilterOutputStream類的子類。BufferedOutputStream來寫入文本的內(nèi)容。希望大家通過本文的學習,對你有所幫助!
本文轉(zhuǎn)載自微信公眾號「Java進階學習交流」,可以通過以下二維碼關(guān)注。轉(zhuǎn)載本文請聯(lián)系Java進階學習交流公眾號。