修剪一棵二叉搜索樹,你會嗎?
如果不對遞歸有深刻的理解,本題有點難。單純移除一個節點那還不夠,要修剪!
修剪二叉搜索樹
力扣鏈接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree/
給定一個二叉搜索樹,同時給定最小邊界L 和最大邊界 R。通過修剪二叉搜索樹,使得所有節點的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改變樹的根節點,所以結果應當返回修剪好的二叉搜索樹的新的根節點。
思路
相信看到這道題目大家都感覺是一道簡單題(事實上leetcode上也標明是簡單)。
但還真的不簡單!
遞歸法
直接想法就是:遞歸處理,然后遇到 root->val < low || root->val > high 的時候直接return NULL,一波修改,趕緊利落。
不難寫出如下代碼:
- class Solution {
- public:
- TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
- if (root == nullptr || root->val < low || root->val > high) return nullptr;
- root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);
- root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high);
- return root;
- }
- };
然而[1, 3]區間在二叉搜索樹的中可不是單純的節點3和左孩子節點0就決定的,還要考慮節點0的右子樹。
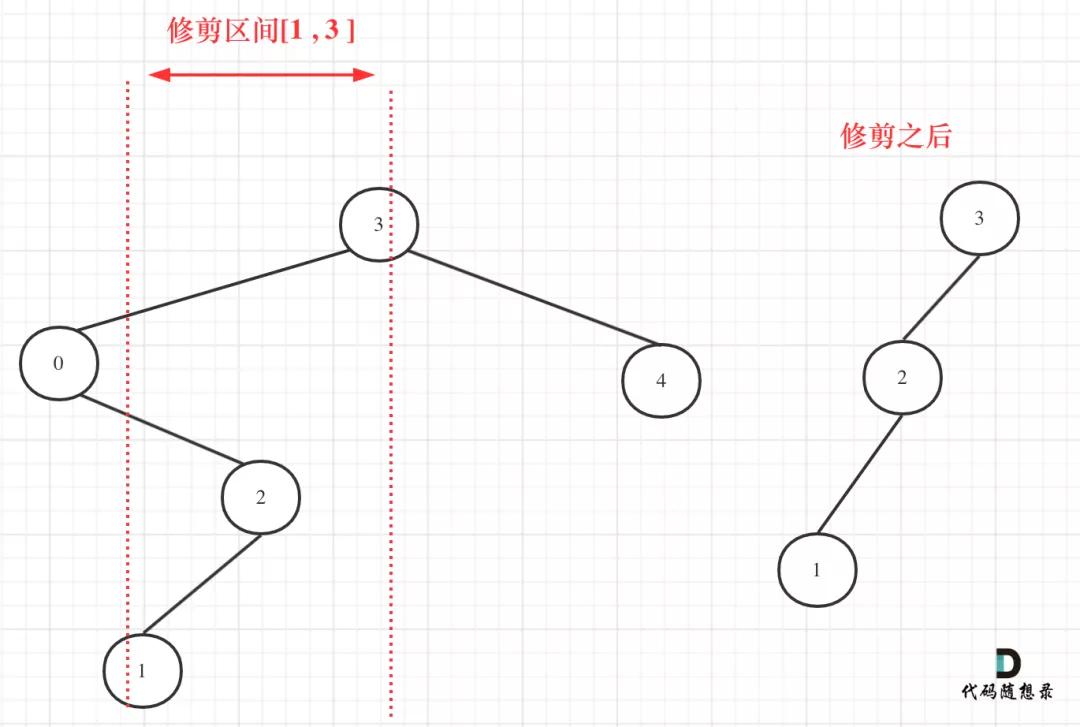
我們在重新關注一下第二個示例,如圖:
669.修剪二叉搜索樹
所以以上的代碼是不可行的!
從圖中可以看出需要重構二叉樹,想想是不是本題就有點復雜了。
其實不用重構那么復雜。
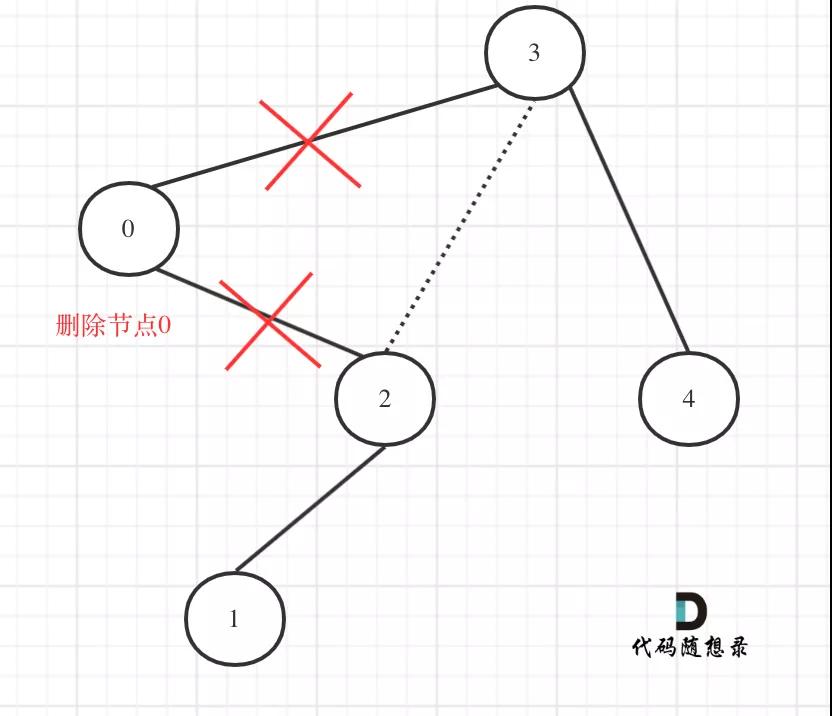
在上圖中我們發現節點0并不符合區間要求,那么將節點0的右孩子 節點2 直接賦給 節點3的左孩子就可以了(就是把節點0從二叉樹中移除),如圖:
669.修剪二叉搜索樹1
理解了最關鍵部分了我們在遞歸三部曲:
- 確定遞歸函數的參數以及返回值
這里我們為什么需要返回值呢?
因為是要遍歷整棵樹,做修改,其實不需要返回值也可以,我們也可以完成修剪(其實就是從二叉樹中移除節點)的操作。
但是有返回值,更方便,可以通過遞歸函數的返回值來移除節點。
這樣的做法在二叉樹:搜索樹中的插入操作和二叉樹:搜索樹中的刪除操作中大家已經了解過了。
代碼如下:
- TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high)
- 確定終止條件
修剪的操作并不是在終止條件上進行的,所以就是遇到空節點返回就可以了。
- if (root == nullptr ) return nullptr;
- 確定單層遞歸的邏輯
如果root(當前節點)的元素小于low的數值,那么應該遞歸右子樹,并返回右子樹符合條件的頭結點。
代碼如下:
- if (root->val < low) {
- TreeNode* right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 尋找符合區間[low, high]的節點
- return right;
- }
如果root(當前節點)的元素大于high的,那么應該遞歸左子樹,并返回左子樹符合條件的頭結點。
代碼如下:
- if (root->val > high) {
- TreeNode* left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // 尋找符合區間[low, high]的節點
- return left;
- }
接下來要將下一層處理完左子樹的結果賦給root->left,處理完右子樹的結果賦給root->right。
最后返回root節點,代碼如下:
- root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // root->left接入符合條件的左孩子
- root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // root->right接入符合條件的右孩子
- return root;
此時大家是不是還沒發現這多余的節點究竟是如何從二叉樹中移除的呢?
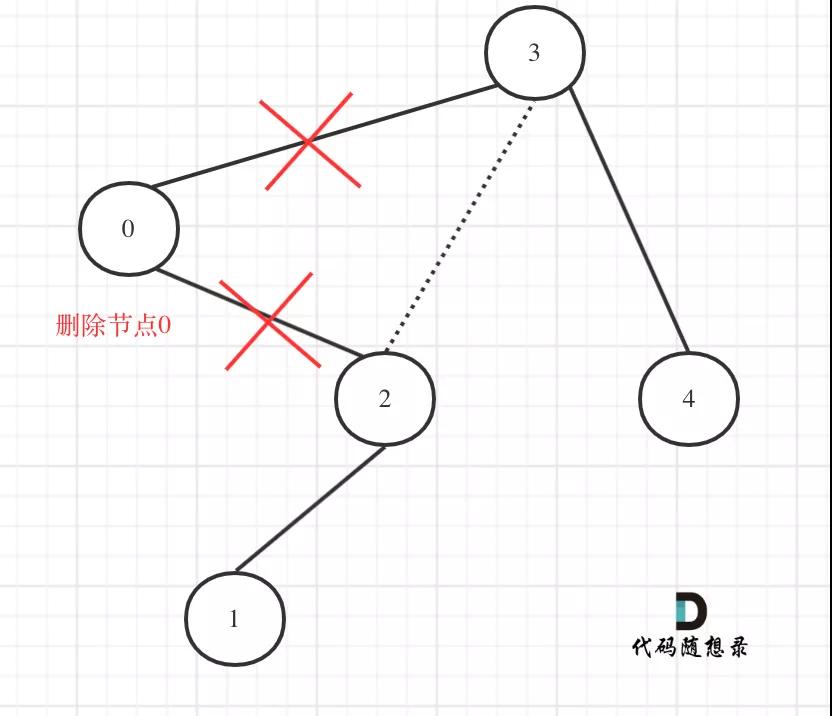
在回顧一下上面的代碼,針對下圖中二叉樹的情況:
669.修剪二叉搜索樹1
如下代碼相當于把節點0的右孩子(節點2)返回給上一層,
- if (root->val < low) {
- TreeNode* right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 尋找符合區間[low, high]的節點
- return right;
- }
然后如下代碼相當于用節點3的左孩子 把下一層返回的 節點0的右孩子(節點2) 接住。
- root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);
此時節點3的右孩子就變成了節點2,將節點0從二叉樹中移除了。
最后整體代碼如下:
- class Solution {
- public:
- TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
- if (root == nullptr ) return nullptr;
- if (root->val < low) {
- TreeNode* right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 尋找符合區間[low, high]的節點
- return right;
- }
- if (root->val > high) {
- TreeNode* left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // 尋找符合區間[low, high]的節點
- return left;
- }
- root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high); // root->left接入符合條件的左孩子
- root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // root->right接入符合條件的右孩子
- return root;
- }
- };
精簡之后代碼如下:
- class Solution {
- public:
- TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
- if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
- if (root->val < low) return trimBST(root->right, low, high);
- if (root->val > high) return trimBST(root->left, low, high);
- root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);
- root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high);
- return root;
- }
- };
只看代碼,其實不太好理解節點是符合移除的,這一塊大家可以自己在模擬模擬!
迭代法
因為二叉搜索樹的有序性,不需要使用棧模擬遞歸的過程。
在剪枝的時候,可以分為三步:
- 將root移動到[L, R] 范圍內,注意是左閉右閉區間
- 剪枝左子樹
- 剪枝右子樹
代碼如下:
- class Solution {
- public:
- TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int L, int R) {
- if (!root) return nullptr;
- // 處理頭結點,讓root移動到[L, R] 范圍內,注意是左閉右閉
- while (root != nullptr && (root->val < L || root->val > R)) {
- if (root->val < L) root = root->right; // 小于L往右走
- else root = root->left; // 大于R往左走
- }
- TreeNode *cur = root;
- // 此時root已經在[L, R] 范圍內,處理左孩子元素小于L的情況
- while (cur != nullptr) {
- while (cur->left && cur->left->val < L) {
- cur->left = cur->left->right;
- }
- cur = cur->left;
- }
- cur = root;
- // 此時root已經在[L, R] 范圍內,處理右孩子大于R的情況
- while (cur != nullptr) {
- while (cur->right && cur->right->val > R) {
- cur->right = cur->right->left;
- }
- cur = cur->right;
- }
- return root;
- }
- };
總結
修剪二叉搜索樹其實并不難,但在遞歸法中大家可看出我費了很大的功夫來講解如何刪除節點的,這個思路其實是比較繞的。
最終的代碼倒是很簡潔。
如果不對遞歸有深刻的理解,這道題目還是有難度的!
本題我依然給出遞歸法和迭代法,初學者掌握遞歸就可以了,如果想進一步學習,就把迭代法也寫一寫。
其他語言版本
Java
- class Solution {
- public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
- if (root == null) {
- return null;
- }
- if (root.val < low) {
- return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
- }
- if (root.val > high) {
- return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
- }
- // root在[low,high]范圍內
- root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
- root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
- return root;
- }
- }
Python
- class Solution:
- def trimBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> TreeNode:
- if not root: return root
- if root.val < low:
- return self.trimBST(root.right,low,high) // 尋找符合區間[low, high]的節點
- if root.val > high:
- return self.trimBST(root.left,low,high) // 尋找符合區間[low, high]的節點
- root.left = self.trimBST(root.left,low,high) // root->left接入符合條件的左孩子
- root.right = self.trimBST(root.right,low,high) // root->right接入符合條件的右孩子
- return root
本文轉載自微信公眾號「代碼隨想錄」,可以通過以下二維碼關注。轉載本文請聯系代碼隨想錄公眾號。