用戶失誤我“買單”:用戶輸入錯(cuò)誤了怎么辦?
本文轉(zhuǎn)載自公眾號(hào)“讀芯術(shù)”(ID:AI_Discovery)
問(wèn)題來(lái)源于生活。上周在做業(yè)余項(xiàng)目時(shí),我遇到了一個(gè)非常有趣的設(shè)計(jì)問(wèn)題:“如果用戶輸入錯(cuò)誤了怎么辦?”如果輸入錯(cuò)誤,就會(huì)發(fā)生以下這種情況:
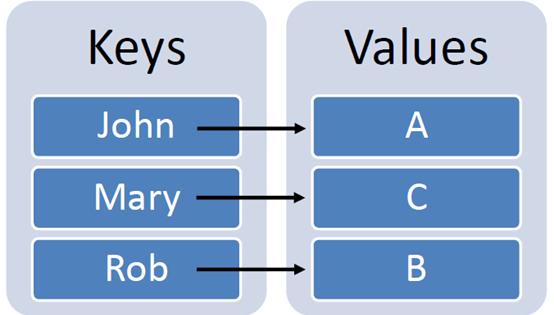
Python中的字典表示 鍵(keys)和值(values)。例如:
- student_grades = {'John': 'A','Mary': 'C', 'Rob': 'B'}# To check grade of John, we call
- print(student_grades['John'])
- # Output: A
當(dāng)您試圖訪問(wèn)不存在的密鑰時(shí)會(huì)遇到什么情況?
- print(student_grades['Maple'])
- # Output:
- KeyError Traceback(most recent call last)
- <ipython-input-6-51fec14f477a> in <module>
- ----> print(student_grades['Maple'])
- KeyError: 'Maple'
您會(huì)收到密匙錯(cuò)誤(KeyError)提示。
每當(dāng)dict()請(qǐng)求對(duì)象為字典中不存在的鍵(key)時(shí),就會(huì)發(fā)生KeyError。接收用戶輸入時(shí),此錯(cuò)誤十分常見(jiàn)。例如:
- student_name =input("Please enter student name: ")
- print(student_grades[student_name])
本文將為你提供幾種處理Python字典 keyerror的方法。去努力構(gòu)建一個(gè)python智能字典,它能幫你處理用戶的輸入錯(cuò)誤問(wèn)題。
設(shè)置默認(rèn)值
一個(gè)非常簡(jiǎn)便的方法便是在請(qǐng)求的key不存在時(shí)返回默認(rèn)值。可以使用get()方法完成此操作:
- default_grade = 'Not Available'
- print(student_grades.get('Maple',default_grade))# Output:
- # Not Available
解決大小寫問(wèn)題
假設(shè)您構(gòu)建了Python字典,其中包含特定國(guó)家的人口數(shù)據(jù)。代碼將要求用戶輸入一個(gè)國(guó)家名并輸出顯示其人口數(shù)。
- # population in millions. (Source: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/population-by-country/)
- population_dict= {'China':1439, 'India':1380, 'USA':331, 'France':65,'Germany':83, 'Spain':46}
- # getting userinput
- Country_Name=input('Please enterCountry Name: ')
- # access populationusing country name from dict
- print(population_dict[Country_Name])
- # Output
- Please enter Country Name: France
- 65
然而,假設(shè)用戶輸入的是‘france’。目前,在我們的字典里,所有的鍵的首字母均是大寫形式。那么輸出內(nèi)容會(huì)是什么?
- Please enter Country Name:france-----------------------------------------------------------------KeyError Traceback (most recentcall last)
- <ipython-input-6-51fec14f477a> in <module>
- 2 Country_Name = input('Pleaseenter Country Name: ')
- 3
- ----> 4 print(population_dict[Country_Name])
- KeyError: 'france'
由于‘france’不是字典中的鍵,因此會(huì)收到錯(cuò)誤提示。
一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的解決方法:用小寫字母存儲(chǔ)所有國(guó)家/地區(qū)名稱。另外,將用戶輸入的所有內(nèi)容轉(zhuǎn)換為小寫形式。
- # keys (Country Names) are now alllowercase
- population_dict = {'china':1439, 'india':1380, 'usa':331, 'france':65,'germany':83, 'spain':46}
- Country_Name=input('Please enterCountry Name: ').lower() # lowercase input
- print(population_dict[Country_Name])
- Please enter Country Name:france
- 65
處理拼寫錯(cuò)誤
然而,假設(shè)用戶輸入的是 ‘Frrance’而不是 ‘France’。我們?cè)撊绾谓鉀Q此問(wèn)題?
一種方法是使用條件語(yǔ)句。
我們會(huì)檢查給定的用戶輸入是否可用作鍵(key)。如不可用,則輸出顯示一條消息。最好將其放入一個(gè)循環(huán)語(yǔ)句中,并在某特殊的標(biāo)志輸入上中斷(如exit)。
- population_dict = {'china':1439, 'india':1380, 'usa':331, 'france':65,'germany':83, 'spain':46}
- while(True):
- Country_Name=input('Please enterCountry Name(type exit to close): ').lower()
- # break from code if user enters exit
- ifCountry_Name=='exit':
- break
- ifCountry_Nameinpopulation_dict.keys():
- print(population_dict[Country_Name])
- else:
- print("Pleasecheck for any typos. Data not Available for ",Country_Name)
循環(huán)將繼續(xù)運(yùn)行,直到用戶進(jìn)入exit。
優(yōu)化方法
雖然上述方法“有效”,但不夠“智能”。我們希望程序功能變強(qiáng)大,并能夠檢測(cè)到簡(jiǎn)單的拼寫錯(cuò)誤,例如frrance和chhina(類似于Google搜索)。
我找到了幾個(gè)適合解決key error的庫(kù),其中我最喜歡的是標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的python庫(kù):difflib。
difflib可用于比較文件、字符串、列表等,并生成各種形式的不同信息。該模塊提供了用于比較序列的各種類和函數(shù)。我們將使用difflib的兩個(gè)功能:SequenceMatcher 和 get_close_matches。讓我們簡(jiǎn)單地瀏覽下這兩種功能。
1. # SequenceMatcher
SequenceMatcher是difflib中的類,用于比較兩個(gè)序列。我們定義它的對(duì)象如下:
- difflib.SequenceMatcher(isjunk=None,a='', b='', autojunk=True)
- isjunk :在比較兩個(gè)文本塊時(shí)用于標(biāo)明不需要的垃圾元素(空白,換行符等)。從而禁止通過(guò)有問(wèn)題的文本。
- a and b: 比較字符串。
- autojunk :一種自動(dòng)將某些序列項(xiàng)視為垃圾項(xiàng)的啟發(fā)式方法。
讓我們使用SequenceMatcher比較chinna和china這兩個(gè)字符串:
- from difflib importSequenceMatcher# import
- # creating aSequenceMatcher object comparing two strings
- check =SequenceMatcher(None, 'chinna', 'china')
- # printing asimilarity ratio on a scale of 0(lowest) to 1(highest)
- print(check.ratio())
- # Output
- #0.9090909090909091
在以上代碼中,使用了ratio()方法。ratio返回序列相似度的度量,作為范圍[0,1]中的浮點(diǎn)值。
2. # get_close_matches
現(xiàn)提供一種基于相似性比較兩個(gè)字符串的方法。
如果我們希望找到與特定字符串相似的所有字符串(存儲(chǔ)于數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)),會(huì)發(fā)生什么情況?
get_close_matches() 返回一個(gè)列表,其中包含可能性列表中的最佳匹配項(xiàng)。
- difflib.get_close_matches(word,possibilities, n=3, cutoff=0.6)
- word:需要匹配的字符串。
- possibilities: 匹配單詞的字符串列表。
- Optional n: 要返回的最大匹配數(shù)。默認(rèn)情況下是3;且必須大于0。
- Optional cutoff:相似度必須高于此值。默認(rèn)為0.6。
潛在的最佳n個(gè)匹配項(xiàng)將返回到一個(gè)列表中,并按相似度得分排序,最相似者優(yōu)先。

來(lái)看以下示例:
- from difflib importget_close_matches
- print(get_close_matches("chinna", ['china','france','india','usa']))
- # Output
- # ['china']
匯總
既然可以使用difflib了,那么讓我們把所有內(nèi)容進(jìn)行組合,構(gòu)建一個(gè)防誤的python字典。
當(dāng)用戶提供的國(guó)家名不在population_dic.keys()中時(shí),需要格外注意。我們應(yīng)嘗試找到一個(gè)名稱與用戶輸入相似的國(guó)家,然后輸出其人口數(shù)。
- # pass country_name in word anddict keys in possibilities
- maybe_country = get_close_matches(Country_Name, population_dict.keys())# Thenwe pick the first(most similar) string from the returned list
- print(population_dict[maybe_country[0]])
最終代碼還需考慮其他一些情況。例如,如果沒(méi)有相似的字符串,或者未向用戶確認(rèn)這是否是所需字符串。如下:
- from difflib importget_close_matches
- population_dict = {'china':1439, 'india':1380, 'usa':331, 'france':65,'germany':83, 'spain':46}
- while(True):
- Country_Name=input('Please enterCountry Name(type exit to close): ').lower()
- # break from code if user enters exit
- ifCountry_Name=='exit':
- break
- ifCountry_Nameinpopulation_dict.keys():
- print(population_dict[Country_Name])
- else:
- # look for similarstrings
- maybe_country =get_close_matches(Country_Name,population_dict.keys())
- if maybe_country == []: # no similar string
- print("Pleasecheck for any typos. Data not Available for ",Country_Name)
- else:
- # user confirmation
- ans =input("Do youmean %s? Type y or n."% maybe_country[0])
- if ans =='y':
- # if y, returnpopulation
- print(population_dict[maybe_country[0]])
- else:
- # if n, start again
- print("Bad input.Try again.")
輸出:
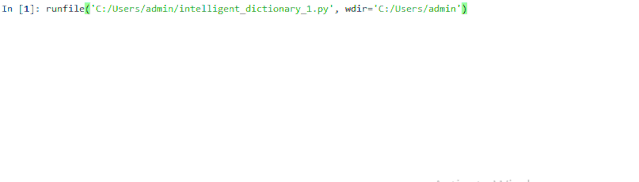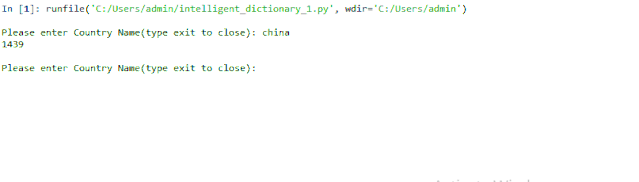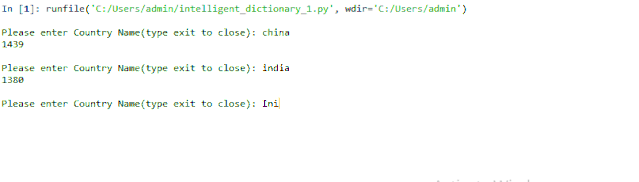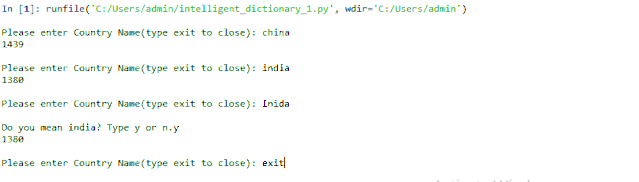
Inida 其實(shí)是India.
這樣一來(lái),用戶的大小寫混淆或是輸入錯(cuò)誤的處理就不在話下了。你還可以進(jìn)一步研究其他各種應(yīng)用程序,比如使用NLPs 更好地理解用戶輸入,并在搜索引擎中顯示相似結(jié)果。Python智能字典的構(gòu)建方法,你學(xué)會(huì)了嗎?