.NET分布式緩存之Memcached執(zhí)行速度檢測
前不久,俺寫了篇文章談到了.Net下面的分布式緩存的一些問題,并結(jié)合DNT里面實現(xiàn)模式發(fā)表了一些自己的看法,近來通過學(xué)習(xí)相關(guān)的東西又有了一些新的體會, 寫在這里作為分布式緩存列系文章的第二部分.
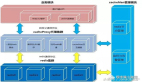
其實對于性的擴展無非是Scale Up(向上擴展)或者是Scale Out(向外擴展), 微軟對此的看法是一個App的緩存***是以它自己為物理邊界進(jìn)行讀寫,而不要放到別處去,這樣帶的問題可能有對象的序列化傳送,反序列化,網(wǎng)絡(luò)連接開銷,跨進(jìn)程的開銷,對于高性能的站點來說都是不能忽視的問題.出于對這些因素的考慮微推薦的作法不是把多個應(yīng)用放在一起在多臺Server布署,而是將一個App劃分成若干個小的應(yīng)用布署到不同的服務(wù)器,下面的關(guān)系圖展示了這種關(guān)系, 這樣每種應(yīng)用就可以獨立管理自己的緩存數(shù)據(jù),但是對于象用戶數(shù)據(jù)這樣的通用數(shù)據(jù)仍然會存在多處.
.NET分布式緩存:兩種解決方案
為了解決緩存同步的問題,有人想出了解決辦法, 可以參考這兩個地方,這個是MS的,這里還有一個,先來看看Peter的這個吧, 主要思想就是把要放到緩存里面的東西加上一層包裝CacheControlItem, 實現(xiàn)代碼請去原文出處下載.
每臺機器都維護(hù)一個WebFarm里面的成員服務(wù)器的列表,如果有新的服務(wù)器進(jìn)來發(fā)現(xiàn)自己不在這個列表中則會通知其它的服務(wù)器把它加到這個名單里面。添加緩存的這程是這樣, A服務(wù)器需要插入一個新的緩存值,它把這個項目插入到自己的緩存中,然后用它初始化一個CacheControlItem并指定它的緩存策略(優(yōu)先級,緩存生存時間),設(shè)定它的動作,即添加,然后把這個結(jié)象序列化通過Web傳送到每一個成員服務(wù)器,接受到這些數(shù)據(jù)的服務(wù)器跟據(jù)這個對象的Action指令,把反序列化后的對象加入到自己的緩存里面,這樣一個同步的過程就完成了,移除緩存對象的過程與之類似,只不過不需要傳送對象,只在包裝類里面設(shè)定它的Action為刪除就可以了. 當(dāng)然,為了提高性能,可以實現(xiàn)一個異步的偵聽線程專門用來響應(yīng)緩存通知的請求. 總體上講這處辦法的效率比較低,在數(shù)據(jù)量較大的情況下可能會造成大量緩存數(shù)據(jù)的同步數(shù)據(jù)流。
我們再來看看M$是怎么做的,它的想法類似,只不過它不在WebFarm的成員服務(wù)器之間同步緩存,而只是保證每臺機器不要讀到已經(jīng)失效的緩存數(shù)據(jù),當(dāng)緩存數(shù)據(jù)失效時(相關(guān)依賴數(shù)據(jù)被更新), 通過維護(hù)一個需要通知的服務(wù)器列表依次調(diào)用每臺服務(wù)器上的WebService,如果當(dāng)前服務(wù)器上存在這鍵值的緩存則使它失效.
這兩個老外寫的東西似乎都比較啰索,不過對初學(xué)者來說比較友好,可以一步步地知道這件事情的來龍去脈,理解會清楚更刻一些。
.NET分布式緩存:Memcached到底有多快?
看了這些如果還不滿意,那么您可以試試Memcached它可以運行在Win32平臺下,在上篇文章中我們已經(jīng)提到了這個東西,但是它在.Net的平臺下面究竟表現(xiàn)如何?是否能象在PHP平臺下面一樣地優(yōu)秀,我們現(xiàn)在來做一個簡單的測試, 對比使用.Net自帶的Cache和Memcached兩種實現(xiàn)方式,看看差距究竟有多大,過程是這樣,分別生成10000個字符串對象并分別設(shè)定鍵值插入到緩存中,然后再取出來,看看花費的總時間. 服務(wù)器端:memcached-1.2.1-win32, 客戶端: memcacheddotnet_clientlib-1.1.5, 服務(wù)器端的使用也比較簡單,解壓文件之后在命令行下面輸入: c:\memcached -d install 先安裝服務(wù), 接著 c:\memcached -d start就可以了,詳細(xì)使用方法見說明文件 -h 是查看幫助, 測試環(huán)境如下:
Memcached服務(wù)器 : Win2003 sp1, Framework 2.0,P4 D 3.4G, 768MB 內(nèi)存, 千兆網(wǎng)卡.
Memcached客戶機 : Win2003 sp1, Framework 2.0,T2060, 1G內(nèi)存( 沙加的神舟筆記本;) ), 千兆網(wǎng)卡.
兩臺機器通過直連線相連.
.Net Cache單機測試 : P4 D 3.4G, 768MB 內(nèi)存.
測試結(jié)果, 存取10000個條目的時間:
- Memcached
- Set(秒) 1.48 1.37 1.48 1.37 1.46
- Get(秒) 2.42 2.42 2.42 2.43 2.42
- HttpRuntime.Cache
- Set(秒) 0.015 0.015 0.015 0.015 0.015
- Get(秒)
- 0.015 0.015 0.015 0.015 0.015
.Net內(nèi)建緩存測試代碼
HttpRuntime.Cache
- protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
- {
- int start = 200;
- int runs = 10000;
- string keyBase = "testKey";
- string obj = "This is a test of an object blah blah es, serialization does not seem to slow things down so much. The gzip compression is horrible horrible performance, so we only use it for very large objects. I have not done any heavy benchmarking recently";
- long begin = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- for(int i = start; i < start+runs; i++)
- {
- HttpRuntime.Cache.Add(keyBase + i, obj,null,System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration,
- TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1),System.Web.Caching.CacheItemPriority.Normal,null);
- }
- long end = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- long time = end - begin;
- Response.Write(runs + " sets: " + new TimeSpan(time).ToString() + "ms<br />");
- begin = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- int hits = 0;
- int misses = 0;
- for(int i = start; i < start+runs; i++)
- {
- string str = (string) HttpRuntime.Cache.Get(keyBase + i);
- if(str != null)
- ++hits;
- else
- ++misses;
- }
- end = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- time = end - begin;
- Response.Write(runs + " gets: " + new TimeSpan(time).ToString() + "ms");
- }
Memcached測試代碼
Memcached
- namespace Memcached.MemcachedBench
- {
- using System;
- using System.Collections;
- using Memcached.ClientLibrary;
- public class MemcachedBench
- {
- [STAThread]
- public static void Main(String[] args)
- {
- int runs = 100;
- int start = 200;
- if(args.Length > 1)
- {
- runs = int.Parse(args[0]);
- start = int.Parse(args[1]);
- }
- string[] serverlist = { "140.192.34.72:11211", "140.192.34.73:11211" };
- // initialize the pool for memcache servers
- SockIOPool pool = SockIOPool.GetInstance();
- pool.SetServers(serverlist);
- pool.InitConnections = 3;
- pool.MinConnections = 3;
- pool.MaxConnections = 5;
- pool.SocketConnectTimeout = 1000;
- pool.SocketTimeout = 3000;
- pool.MaintenanceSleep = 30;
- pool.Failover = true;
- pool.Nagle = false;
- pool.Initialize();
- MemcachedClient mc = new MemcachedClient();
- mc.EnableCompression = false;
- string keyBase = "testKey";
- string obj = "This is a test of an object blah blah es, serialization does not seem to slow things down so much. The gzip compression is horrible horrible performance, so we only use it for very large objects. I have not done any heavy benchmarking recently";
- long begin = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- for(int i = start; i < start+runs; i++)
- {
- mc.Set(keyBase + i, obj);
- }
- long end = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- long time = end - begin;
- Console.WriteLine(runs + " sets: " + new TimeSpan(time).ToString() + "ms");
- begin = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- int hits = 0;
- int misses = 0;
- for(int i = start; i < start+runs; i++)
- {
- string str = (string) mc.Get(keyBase + i);
- if(str != null)
- ++hits;
- else
- ++misses;
- }
- end = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- time = end - begin;
- Console.WriteLine(runs + " gets: " + new TimeSpan(time).ToString() + "ms");
- Console.WriteLine("Cache hits: " + hits.ToString());
- Console.WriteLine("Cache misses: " + misses.ToString());
- IDictionary stats = mc.Stats();
- foreach(string key1 in stats.Keys)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(key1);
- Hashtable values = (Hashtable)stats[key1];
- foreach(string key2 in values.Keys)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(key2 + ":" + values[key2]);
- }
- Console.WriteLine();
- }
- SockIOPool.GetInstance().Shutdown();
- }
- }
- }
結(jié)論
通過這個對比測試我們可以看出內(nèi)建的Cache比使用Memcached要快出約130倍,但是從總體速度上來看Memcached并不慢,這兩種方式可以在項目中有選擇性地結(jié)合使用可以產(chǎn)生很棒的效果.并且Memcached可使用的內(nèi)存數(shù)量要多得多,同時也可以做集群避免單點問題.
以上就介紹了.NET分布式緩存之Memcached的速度檢測。本文來自沙加的博客:《.Net下的分布式緩存(2)--實現(xiàn)分布式緩存同步的手段》
【編輯推薦】